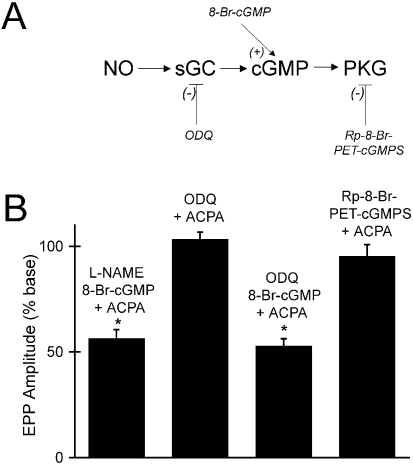
Fig. 6.
Nitric oxide (NO) is required to increase cGMP synthesis and activate protein kinase G. (A) The NO-cGMP signalling pathway. NO-stimulated soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) and cGMP-dependent protein kinase-1 (PKG). 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ) is an inhibitor of sGC, Rp-B-Phenyl-1, N2-etheno-8-bromoguanosine 3’,5’-cyclic monophosphorothioate (Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPS) is an inhibitor of PKG and 8-Br-cGMP is a membrane-permeable analogue of cGMP. (B) Mean percent reduction of end-plate potential (EPP) amplitudes following application of arachidonylcyclopropylamide (ACPA) (10 µm). ACPA was applied with Nω-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) (0.3 mm) and 8-Br-cGMP (40 µm, n = 6) with ODQ (50 µm, n = 4), ODQ and 8-Br-cGMP (n = 4) and Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPS (30 µm, n = 4). *The mean EPP amplitude is significantly different from its measurement under baseline conditions (P < 0.05; Student's t-test). Baseline EPP measurements were made in the presence of L-NAME and 8-Br-cGMP, ODQ, ODQ and 8-Br-cGMP, or Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPS, respectively. Error bars represent SEM.