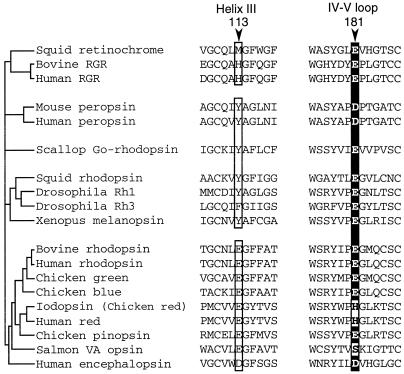
Figure 3.
Comparison of amino acids at position 113 and 181. Phylogenetic relationships among the members of the rhodopsin family are schematically represented based on previous reports (9–11). All the members of vertebrate-rhodopsin group possess a glutamic or aspartic acid at position 113 in helix III, whereas retinochrome or invertebrate-rhodopsin groups do not. On the other hand, all have a glutamic or aspartic acid at position 181 in the extracellular IV–V loop, except for the long-wavelength visual pigments (iodopsin and human red) and VA opsins. Note that Tyr-113 is neutral in the case of invertebrate octopus rhodopsin (19). GenBank accession numbers for the respective sequences are; for squid retinochrome, X57143; for bovine retinal G protein-coupled receptor, S67535; for human retinal G protein-coupled receptor, U15790; for mouse peropsin, AF012271; for human peropsin, AF012270; for scallop Go-rhodopsin, AB006455; for squid rhodopsin, X70498; for Drosophila Rh1, K02315; for Drosophila Rh3, Y00043; for Xenopus melanopsin, AF014797; for bovine rhodopsin, K00506; for human rhodopsin, U49742; for chicken green, M92038; for chicken blue, M92037; for iodopsin (chicken red), X57490; for human red, M13305; for chicken pinopsin, U15762; for salmon VA opsin, AF001499; and for human encephalopsin, AF140242.