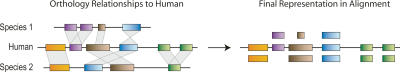
Figure 2.
“Human-centric” approach for constructing multisequence alignments. The human sequence (middle) is aligned to two other species’ sequences (top and bottom). In the final alignment (right), nucleotides from the other species need not have retained their original order and orientation; they may, for example, have been subjected to inversions (top blue) or duplications (bottom green). Non-human duplications need to be resolved (top magenta), so that each position in the human sequence is aligned to at most one position in any other species’ sequence.