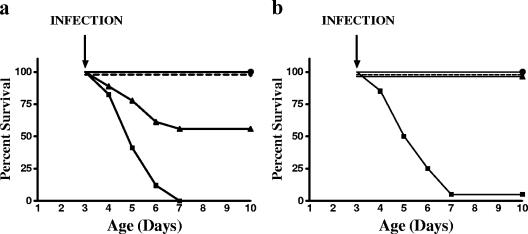
FIG. 2.
(a) Survival curves for rat pups receiving lysostaphin treatment. •, noninfected pups treated with lysostaphin (n = 17); ⧫, S. aureus-infected pups with lysostaphin treatment beginning 30 min after infection (n = 22); ▴, S. aureus-infected pups with lysostaphin treatment beginning 6 h after infection (n = 19); ▪, S. aureus-infected and untreated pups (n = 17). Lysostaphin treatment significantly improved survival in infected rats treated 30 min (P < 0.00001) and 6 h (P < 0.0044) after S. aureus infection. Lysostaphin treatment without infection had no associated morbidity. (b) Survival curves for S. aureus-infected rat pups receiving lysostaphin (•) (n = 18), vancomycin (⧫) (n = 18), oxacillin (n = 20) (▴), or normal saline (▪) (n = 16) 30 min after infection are shown. Each antibiotic treatment group was significantly different from saline-treated infected pups (P < 0.00001).