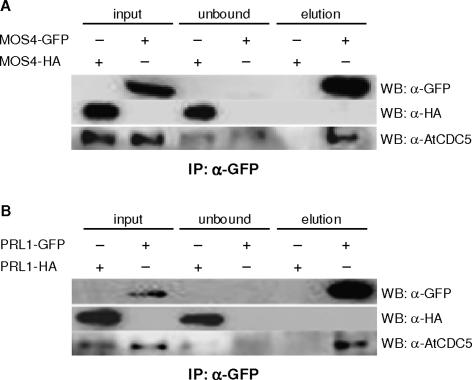
Figure 4.
MOS4, AtCDC5, and PRL1 interact in planta. (A) AtCDC5 coimmunoprecipitates with MOS4-GFP in nuclear extracts from mos4-1 complemented by gMOS4-GFP transgenic plants. (B) AtCDC5 coimmunoprecipitates with PRL1-GFP in nuclear extracts from prl1-1 complemented by gPRL1-GFP transgenic plants. The aerial plant tissue was harvested for nuclear fractionation, and nuclear extracts were subjected to IP as indicated. Equal amounts by number of nuclei in nuclear extracts (input) and flow-through supernatant after IP (unbound) were loaded for immunoblotting. The elution fraction for immunoblotting with anti-GFP or anti-HA antibody was ∼20 times more concentrated than the nuclear extract, and that of anti-AtCDC5 antibody was ∼40 times more concentrated. Protein from MOS4-HA (A) and PRL1-HA (B) transgenic plants were used as negative controls in anti-GFP IPs.