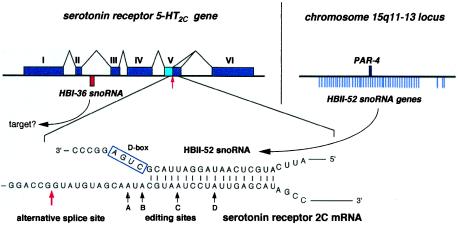
Figure 4.
Structure of the serotonin receptor 5-HT2Cgene containing the intron-encoded HBI-36 gene (Upper Left) and potential base-paired interaction between the serotonin receptor 5-HT2C mRNA and C/D box snoRNA HBII-52 (Lower). (Upper Left) The six exons of the 5-HT2C gene including the alternative splice site in exon V are indicated with the location of the HBI-36 snoRNA gene within the second intron shown by a red bar (most introns of the 5-HT2C gene are extremely large; not drawn to scale). (Upper Right) Location of 47 copies of the HBII-52 snoRNA genes with respect to the PAR-4 gene in the PWS locus on chromosome 15 (see Fig. 3A) is indicated on the right. (Lower) Potential base pairing of HBII-52 snoRNA with the editing sites/alternative splice site of exon V. The corresponding guide duplex should direct ribose methylation to the nucleotide paired to the fifth nucleotide upstream from box D (4–7), i.e., the adenosine at position C. The adenosine at position C is one out of four sites of adenosine-to-inosine editing within the serotonin receptor mRNA (ref. 37; the four sites of edition in 5-HT2C receptor mRNA are denoted by solid arrows and labeled A–D). The alternative splicing site present in the serotonin receptor 5-HT2C mRNA (36) is indicated by a red arrow.