Figure 2.
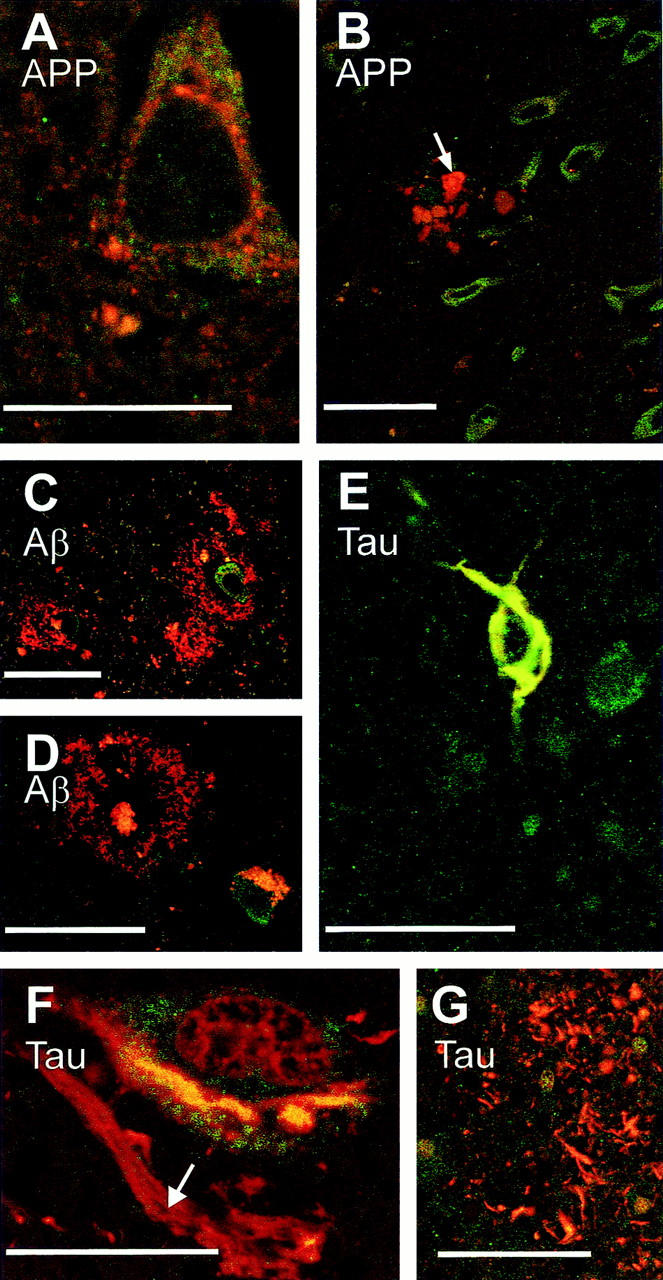
Immunofluorescence of FE65, APP, β-amyloid, and tau proteins. Double-immunofluorescent labeling (green, FE65; red, APP, β-amyloid, or tau) did not reveal co-localization of FE65 and APP in the cell body of neurons (A) nor was FE65 detected in APP-positive dilated neurites surrounding plaques (B, arrow indicates dilated neurites; note the vicinity of numerous green labeled FE65 immunopositive neurons), in diffuse β-amyloid deposits (C) and classical senile plaques (D, note that, in this material that was not treated with Sudan black, lipofuscine accumulated in a neuron). Double-tau-FE65 labeling underlines a co-localization of these two proteins in neurofibrillary tangles, an example of which is shown in E. FE65 and tau, however, were not co-localized in other neurofibrillary alterations (F, ghost tangle indicated by an arrow in the neighborhood of a neuron bearing a yellow double-labeled tangle; G, neurites of the senile crown). Scale bars, 25 μm (A and F) and 50 μm (B–E and G).
