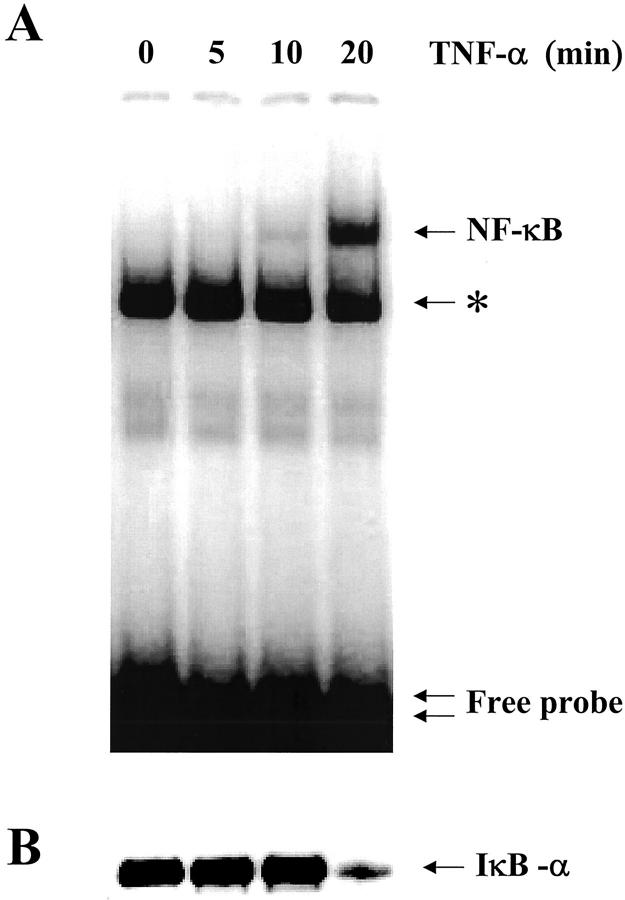
Figure 1.
Time-course of NF-κB translocation and IκBα degradation in non-CF Beas2B cells exposed to TNF-α. A: EMSA analysis of NF-κB binding activity in nuclear extracts from Beas2B cells treated for the indicated time with 100 U/ml TNF-α. TNF-α induced the increase in NF-κB binding activity in nuclear extracts in a time-dependent manner. Maximal nuclear translocation was reached after 20 minutes in the presence of TNF-α. The single arrow corresponds to binding of NF-κB to the probe, and the double arrow indicates the free probe. Nonspecific binding of the NF-κB probe can also be seen on the EMSAs (asterisk). Competition with 100× excess of cold competitors (see Materials and Methods) abolished binding of NF-κB to the probe but not the nonspecific binding. B: Detection of IκBα by Western blot analysis of cytoplasmic extracts from Beas2B cells exposed to TNF-α. TNF-α rapidly induced the degradation of IκBα, in parallel to NF-κB translocation. The arrow indicates the IκBα band at ∼36 kd.