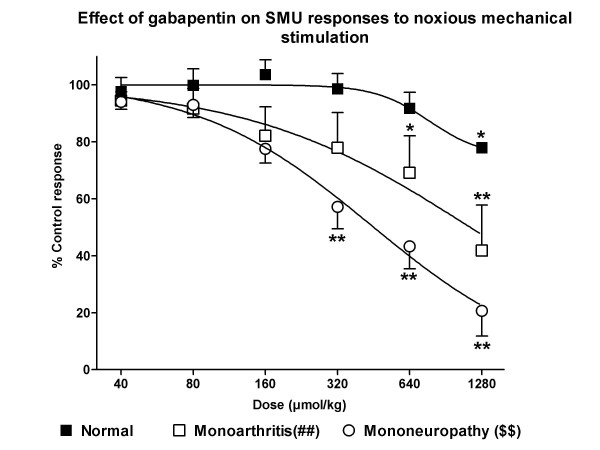
Figure 4.
Antinociceptive effect of gabapentin in responses to noxious mechanical stimulation. The iv. administration of gabapentin induced a dose-dependent inhibition of responses to noxious mechanical stimulation in arthritic and neuropathic rats, but not in normal rats. The calculated ID50s were of 1,145 ± 14 μmol/kg (200 mg/kg) in arthritis and 414 ± 27 μmol/kg (73 mg/kg) in neuropathy (P < 0.001, two tail unpaired t-test). The effect was still significant 30 min after the administration of gabapentin. Statistical comparison of the regression curves showed a significant difference between normal and arthritic animals (P < 0.01; ##) and between arthritic and neuropathic rats (P < 0.01; $$).*P < 0.05, *P < 0.01, comparison vs. control response with the one-way ANOVA, with the post-hoc Tukey test.