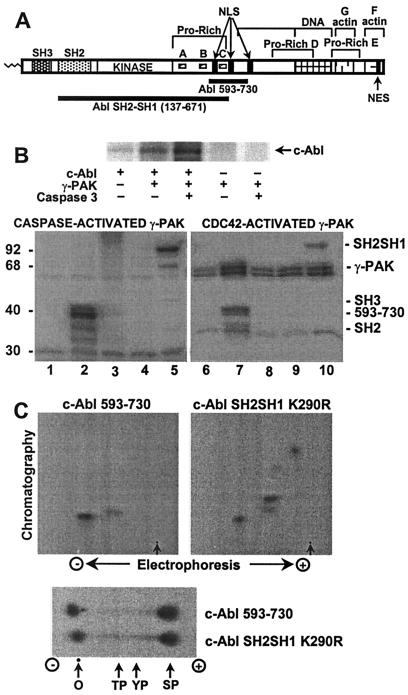
Figure 2.
Phosphorylation of c-Abl by γ-PAK in vitro. (A) A cartoon of the c-Abl domains SH3, SH2, kinase, and the C-terminal domain. The latter contains proline-rich sequences A, B, C, D, and E; three nuclear localization signals (NLS); one nuclear export signal (NES); and DNA-binding and actin-binding domains. The Crk/CrkL family of CF adaptor proteins binds to proline-rich sequences A and B, whereas the Nck and Abi adaptors bind to proline-rich sequence C. (B, Upper) c-Abl expressed in insect cells was immunoprecipitated and phosphorylated with γ-PAK activated by caspase 3 as described in Experimental Procedures and analyzed by SDS/PAGE. (B, Lower) GST-fusion proteins of c-Abl fragments were phosphorylated with activated γ-PAK and subjected to SDS/PAGE. Lanes 1 and 6, no substrate; lanes 2 and 7, c-Abl 593–730; lanes 3 and 8, c-Abl SH2; lanes 4 and 9, c-Abl SH3; lanes 5 and 10, c-Abl SH2–SH3 K290R. (C, Upper) Tryptic phosphopeptide mapping was carried out on Abl 593–730 and Abl SH2–SH1 K290R phosphorylated by γ-PAK. Arrows indicate the origin. (C, Lower) Phosphoamino acid analysis of Abl 593–730 and Abl SH2–SH1 K290R phosphorylated by γ-PAK. In all instances, radiolabeled phosphate was detected by using a PhosphorImager system. O, origin; TP, phosphothreonine; YP, phosphotyrosine; SP, phosphoserine.