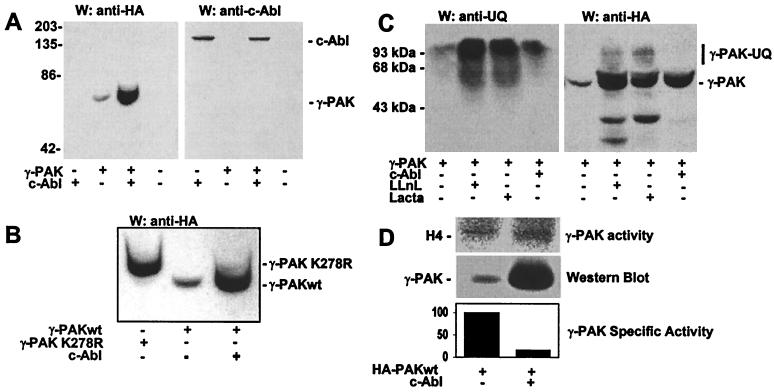
Figure 4.
c-Abl induces γ-PAK accumulation and inactivation. (A) Western blots of lysates from cells transfected with c-Abl, HA-γ-PAK, or both enzymes using anti-HA antibodies (Left) or anti-Abl antibodies (Right). (B) Western blots of lysates of cells transfected with HA-γ-PAK K278R, HA-γ-PAKwt, or HA-γ-PAKwt and c-Abl using anti-HA antibodies. (C) Western blots using anti-ubiquitin (Left) or anti-HA antibodies (Right) of total extracts from cells transfected with HA-γ-PAK and treated for 9 h with 50 μM LLnL or 10 μM lactacystin (Lacta). Nontreated cells and cells coexpressing c-Abl are shown for comparison. UQ, ubiquitin. (D) Following immunoprecipitation with HA antibody from cells transfected with HA-γ-PAK alone or with c-Abl, γ-PAK activity was assayed with H4. γ-PAK protein was detected simultaneously by Western blotting with anti-HA antibody. Mean activation of three independent experiments is shown.