Figure 2.
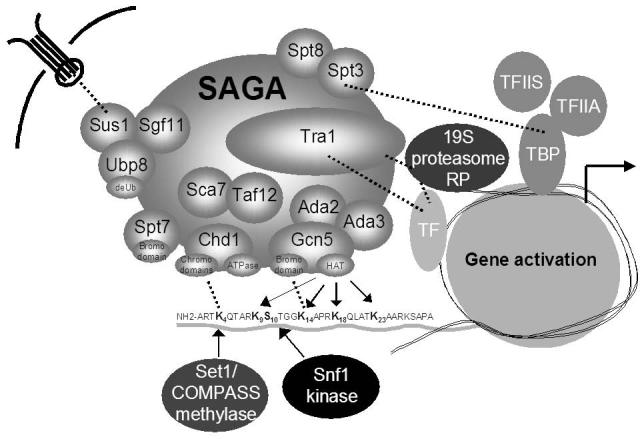
Multi-tasking on chromatin with the SAGA coactivator complexes. SAGA and SLIK subunits are organized into modules that carry out distinct functions. Shown is a representation of SAGA recruited to a promoter functioning in transcriptional activation. Tra1 associates with DNA-binding transcription factor/activator (TF) proteins and this interaction is strengthened by the 19S proteasome regulatory particle (RP). Set1-mediated H3-K4 methylation and Snf1-mediated H3-S10 phosphorylation promote the HAT activity of Gcn5. The bromo- and chromodomains within SAGA mediate additional chromatin interaction through association with modified histone lysines. The Ubp8/Sgf11/Sus1 module functions in H2B deubiquitination as well as mRNA export through interaction with pores within the nuclear membrane. Ada2 and Ada3, as well as Sca7, Taf12, and Chd1 function, in part, to regulate Gcn5-mediated HAT activity. The Spt3/Spt8 module interacts with the TATA-binding protein (TBP), and TBP and SAGA together interact strongly with the general transcription factor TFIIA and the elongation factor TFIIS. The histone H3 N-terminal tail is shown to illustrate interaction of SAGA with multiple resides, indicated by position number, within the peptide. Dotted lines indicate interactions, while arrows indicate enzymatic activities.
