Figure 5.
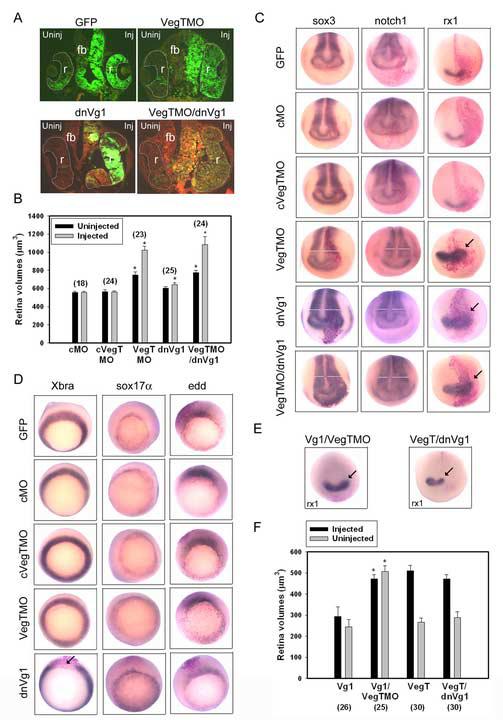
Reduction of VegT and Vg1 in the D1.1 lineage increases the size of the neural ectoderm.
(A) Reduction of VegT by morpholino injection (VegTMO) and of Vg1 by expression of a dominant-negative construct (dnVg1) enlarged the retina (r) and forebrain (fb). Note the abundant D1.1 progeny (green) in both structures (cf. Fig. 2E). Reduction of both factors (VegTMO/dnVg1) resulted in a similar phenotype.
(B) The mean volumes of retinas in embryos in which control morpholinos (cMO, cVegTMO) were injected are not different from GFP controls (Fig. 2B). Those from VegTMO-injected embryos are significantly larger on both sides, and those from dnVg1-injected embryos are significantly larger on the injected side. Those from embryos injected with both constructs (VegTMO/dnVg1) are larger than for dnVg1 alone and similar to those from VegTMO alone. * indicates p<0.01 compared to GFP controls. Numbers in parentheses indicate size of sample.
(C) The expression domains of pan-neural plate (sox3, notch1; white bars indicate measurement of width of domain) and retinal (rx1; arrows) genes are expanded on the side (right) injected with VegTMO or dnVg1. The expansion of neural plate markers is somewhat enhanced in embryos co-injected with VegTMO and dnVg1 (see also Table 1).
(D) The expression domains of mesodermal (Xbra) and endodermal (sox17α, edd) genes after injection into D1.1 of the constructs indicated on the left. The only notable effect is repression of Xbra by dnVg1 (arrow).
(E) The expansion of rx1 expression (arrow) by VegTMO is not altered by co-expression of Vg1, whereas the expansion caused by dnVg1 is reversed by co-expression of VegT.
(F) The small retinal volumes displayed by Vg1-injected embryos were significantly increased by co-injection of VegTMO (* indicates p<0.01). The small retinal volumes displayed by VegTMO-injected embryos were not altered by co-injection of dnVg1 (p>0.05).
