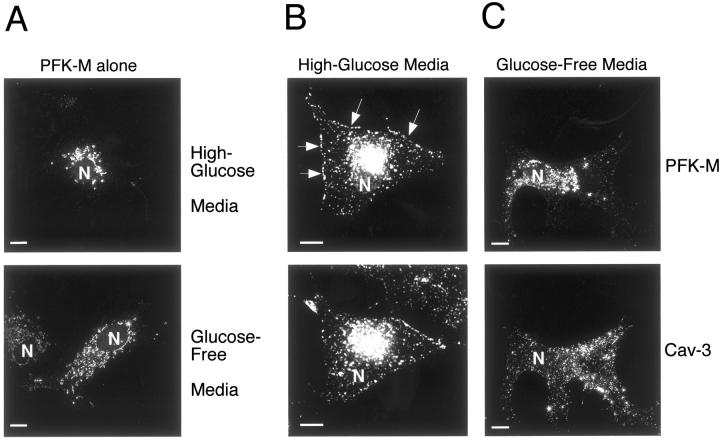
Figure 5.
PFK-M membrane recruitment is dependent on the presence of extracellular glucose. Cos-7 cells were transfected with the cDNA encoding V5-tagged PFK-M, alone or in combination with Cav-3. Thirty-six hours after transfection, cells were incubated for 1 hour either with glucose-free media or with high-glucose media. Cells were then formaldehyde-fixed and immunostained with a monoclonal antibody directed against the V5 epitope tag (A) or doubly immunostained with anti-V5 mAb and anti-Cav-3 pAb (B and C). Note that glucose depletion of cells expressing PFK-M alone has no significant effect on the distribution of PFK-M (A, bottom), as compared to cells expressing PFK-M alone incubated in high-glucose media (A, top). However, incubation of cells expressing Cav-3 and PFK-M in glucose-free media for 1 hour clearly impedes the targeting of PFK-M to the plasma membrane (C). Under these conditions, the distribution of PFK-M remains perinuclear. In contrast, when cells expressing Cav-3 and PFK-M were incubated in high-glucose media, Cav-3 expression induces the membrane recruitment of PFK-M. (B). Arrows point at the plasma membrane. These results suggest that the membrane recruitment of PFK-M is dependent on the presence of extracellular glucose and on Cav-3 expression. N, Nucleus. Note that high-glucose media contains 4.5 g of glucose per L; this is the normal concentration of glucose that is routinely used in high-glucose DME for cell culture. Scale bars, 10 μm.