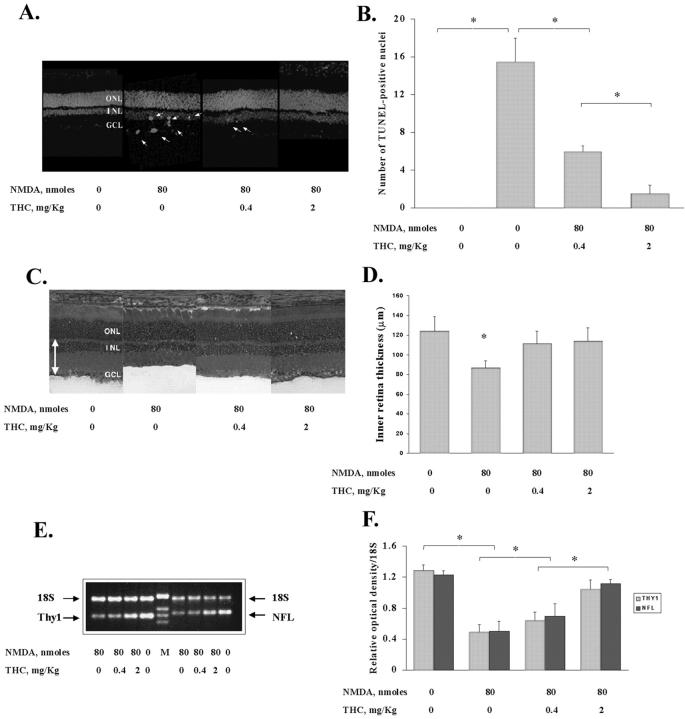
Figure 3.
NMDA-induced retinal neurotoxicity is prevented by THC. Rats were given an intravenous injection of THC suspension immediately before the intravitreal injection of NMDA. The effect of systemic THC (0.4 or 2 mg/kg) on the NMDA (80 nmol/eye)-induced retinal neurotoxicity is determined by TUNEL analysis at 18 hours after NMDA injection and by measurement of inner retinal thickness and Thy-1 and NF-L mRNA at day 7 of NMDA injection. A: Representative retinal distribution of NMDA-induced TUNEL-positive cells in retinal sections after injection of THC at two levels. OCT-frozen eye sections perpendicular to the retinal surface were analyzed as described before. B: Dose-dependent effect of THC on the NMDA-induced TUNEL-positive cells. Values represent the mean ± SE of a total of three animals for each group in three experiments. *, Significant at P < 0.01. C: Representative H&E-stained retinal cryosections (8 μm) showing the relative inner retinal thickness. OCT-frozen eye sections perpendicular to the retinal surface were measured at two adjacent locations as described before. The thickness of the inner retina (double-headed arrow) was measured by the distance between the inner limiting membrane and the inner border of outer nuclear layer. D: Relative inner retinal thickness analysis to show the loss of inner retinal thickness and protection by THC. Readings from three to four sections from each eye were averaged to obtain the mean value for that eye. All values represent the mean ± SE of a total of four animals for each group in two experiments. *, Significant at P < 0.05. E: Representative negative image of ethidium bromide-stained agarose (2%) gel indicating the level of 18S rRNA relative to Thy-1 or NF-L message in the retina total RNA. F: NMDA-induced reduction of Thy-1 and NF-L mRNA and dose-dependent protection by THC. Values represent the mean ± SE of four experiments. *, Significant at P < 0.05.