Figure 5.
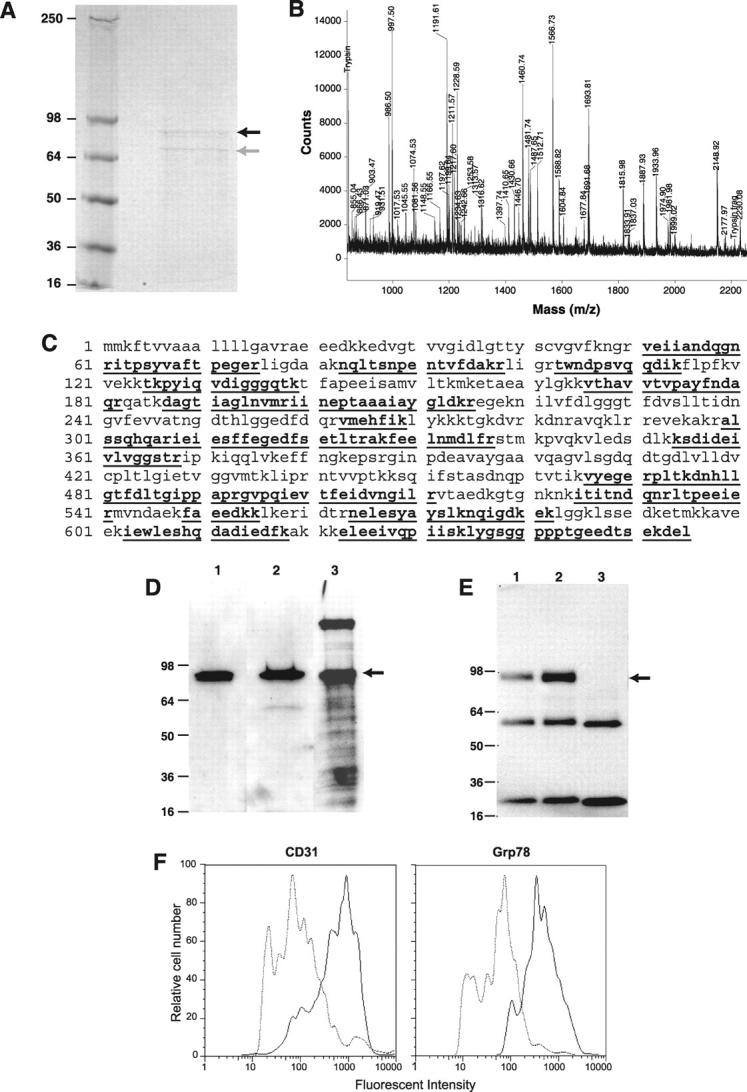
Characterization of Grp78 as a target for CAPGPSKSC peptide. A: The Coomassie-stained gel after protein affinity purification on an immobilized CAPGPSKSC column. The black arrow indicates a protein band of ∼82 kd and the gray arrow indicates a proteolytic product of the ∼82-kd protein. B: The cryptic peptide mixture of the ∼82-kd protein band analyzed by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometer. C: The matched cryptic peptide sequences of the ∼82-kd protein band in mouse Grp78 (shown in bold and underlined). D: The Western blotting of the enriched bEND.3 membrane extract with antibodies against 1) the N-terminus of Grp78, 2) the C-terminus of Grp78, and 3) by peptide-ligand blot using biotinylated CAPGPSKSC. E: Immunoprecipitation of the enriched bEND.3 membrane extract with antibodies against 1) the N-terminus of Grp78, 2) the C-terminus of Grp78, 3) a control antibody (anti-tissue factor). Blotting was performed using biotinylated CAPGPSKSC peptide. The lower bands are immunoglobulin fragments in the reaction. F: The flow cytometry analysis of cell surface Grp78 molecules on bENd.3 cells using anti-Grp78 polyclonal antisera. Note a shift of fluorescent intensity in cells stained with anti-Grp78 antisera, similar to cells stained with anti-CD31 antibody.
