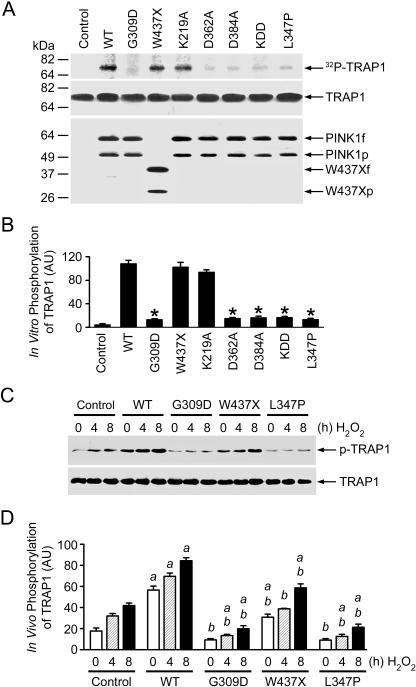
Figure 3. Phosphorylation of TRAP1 by Wild-Type and Mutant PINK1.
(A) In vitro kinase assays were performed by incubation of purified TRAP1 with [γ32-P] ATP in the absence (control) or presence of FLAG-tagged wild-type (WT) or mutant PINK1 proteins as indicated. Phosphorylated TRAP1 was visualized by autoradiography (top panel). PINK1 and TRAP1 proteins used in the kinase assays were shown by immunoblotting with anti-TRAP1 (middle panel) and anti-FLAG antibodies (bottom panel).
(B) Normalized levels of in vitro TRAP1 phosphorylation by wild-type or mutant PINK1. Data represent mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) from three independent experiments. *Significantly different from the wild-type PINK1 (p < 0.01).
(C) PC12 cells expressing wild-type or mutant PINK1 or vector-transfected controls were treated with 400 μM H2O2 as indicated. In vivo phosphorylation of endogenous TRAP1 was determined by immunoprecipitation with anti-TRAP1 antibody followed by immunoblotting using anti-phosphoserine (upper panel) and anti-TRAP1 (lower panel) antibodies.
(D) Normalized levels of in vivo TRAP1 phosphorylation by wild-type or mutant PINK1. Data represent mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. aSignificantly different from the corresponding H2O2-treated vector-transfected controls (p < 0.01). bSignificantly different from the wild-type PINK1-transfected cells (p < 0.01).
AU, arbitrary units.