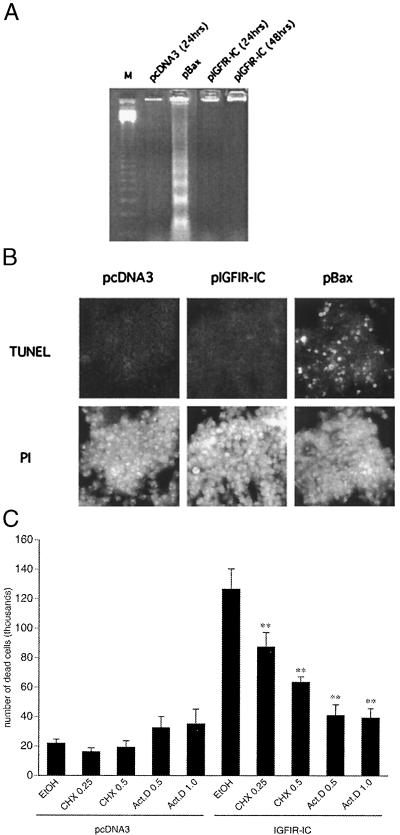
Figure 2.
IGFIR-IC-induced cell death is nonapoptotic. (A) Internucleosomal DNA fragmentation of cells transfected as in Fig 1. Soluble DNA was extracted from cells 24 or 48 h after transfection. Whereas the Bax-transfected cells demonstrated internucleosomal DNA fragments, the chromatin in IGFIR-IC transfected cells remained intact at 24 and 48 h after transfection. (B) TUNEL staining of cells transfected as in A. Cells were assayed 48 h after transfection. (Upper) FITC staining of the TUNEL labeling. Bax, but not IGFIR-IC, transfected cells show TUNEL-positive staining. (Lower) The same fields of cells stained with propidium iodide (PI). Cells were permeabilized before staining. Similar results were obtained at 24 h. (C) Transcription and protein synthesis are required for IGFIR-induced cell death. Actinomycin D (Act.D) or cycloheximide (CHX) (numbers represent μg/ml) were added 8.5 h after the transfections, and the medium was replaced after 12 h with fresh medium without drugs. Floating cells were collected after 24 h and counted in the presence of trypan blue. Control samples were treated with solvent only (ethanol 0.05%). The expression of IGFIR-IC at the time of administration of the drugs was comparable to the expression at 24 h, as assessed by Western blot analysis. The error bars represent the SEM of four independent experiments. Within the samples transfected with pIGFIR-IC, the asterisks indicate a highly significant difference (P = 0.0011 for 0.25 μg/ml CHX, and P < 0.0001 for 0.5 μg/ml CHX, and 0.5 μg/ml and 1 μg/ml Act.D; Bonferroni/Dunn posthoc test) from the pIGFIR-IC transfected sample treated with solvent only (EtOH), as determined by one-way ANOVA (F = 20.727; P < 0.0001).