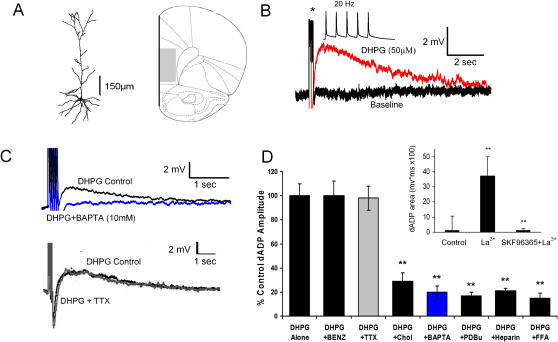
Figure 10. Deep layer 5 pyramidal PFC neurons show a burst-induced nonselective cation current-mediated slow afterdepolarization following activation of group 1 mGluR receptors.
(A) Camera lucida reconstruction of a deep layer 5 pyramidal neuron from the PFC (left). (Right) schematic showing the PFC (infralimbic and prelimbic), shaded area where recordings were taken. (B) The group 1 mGluR agonist DHPG (50uM) induced a 20Hz burst-triggered (Inset) dADP (Red) compared to baseline before DHPG application to the bath. (C) (top) Intracellular Ca2+ chelation with BAPTA (10 mM; Blue) for 10 min after establishing whole-cell configuration substantially reduced the dADP induced by a 20 Hz burst and DHPG (50 uM)+BAPTA (10mM) immediately after establishing whole-cell configuration. (bottom) Bath application of the voltage-gated Na+ channel blocker, TTX (1 µM, Gray) for 10 min and elimination of action potentials at intensities 10 times the rheobase had no effect on the dADP induced by a 20 Hz burst and DHPG (50 uM)+TTX (1 µM). (D) The effects of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger blocker benzamil (100 µM); Na+ ion 80% replacement with choline chloride; voltage-gated Na+ channel blocker, TTX (1 µM); intracellular Ca2+ chelation with BAPTA (10 mM); PKC activation with PdBU (1 µM),; IP3 receptor blockage with heparin (2 mg/ml); and nonselective cation channel blockade with flufenamic acid (100 µM) on the DHPG-(50 µM) and burst-induced dADP. (n>5, **p<0.01) (Inset) The TRPC4/5 potentiator, La3+ (100 µM) induced a small burst triggered (5 action potentials @ 20 Hz) dADP in the absence of mGluR activation and was blocked by the broad spectrum nonselective cation channel blocker, SKF96365 (100 µM). (n>5, **p<0.01)