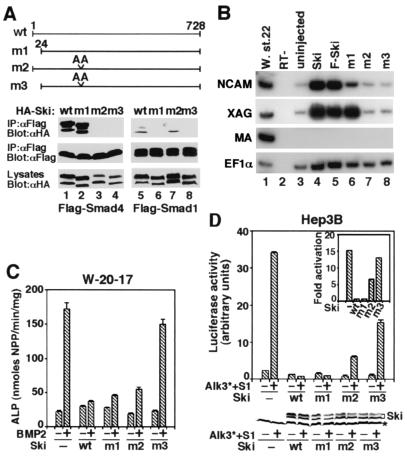
Figure 5.
Interactions between Ski and the Smads are required for repression of BMP signaling by Ski. (A) Interaction between mutant Ski proteins and the Smads. (Upper) Schematic drawings of the Ski mutants are shown. (Lower) HA-tagged, wild-type, or mutant Ski proteins were cotransfected into 293T cells together with Flag-tagged Smad1 or Smad4 as indicated. The Smad-bound Ski proteins were isolated by immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag M2 mAb and detected by Western blotting with an anti-HA mAb. Cell lysates were blotted directly as a control for HA-Ski expression. (B) Mutant analysis in Xenopus ectoderm. Explants were harvested at stage 22 and assayed for NCAM, XAG, and muscle actin expression. Lanes 1 and 2, whole embryo and no RT (RT−) control; lane 3, uninjected sample; lanes 4 and 5, explants expressing 500 pg of wild-type ski mRNA; lanes 6–8, explants expressing 500 pg of mRNA of ski mutants m1, m2, or m3. (C) To test the ability of the Ski mutants to repress BMP-induced ALP activity, various ski mutants were transfected into W-20-17 cells. ALP activity was assayed as described in Materials and Methods. (D). Hep3B cells were cotransfected with 0.75 μg of 15xGCCG-Luc, 0.5 μg of constitutive active BMPRI (Alk3*), 0.75 μg of HA-tagged, wild-type, or mutant ski, and 0.15 μg of Smads. Luciferase activity was measured 48 h later. (Lower) The levels of Ski proteins present in the transfected cells were detected by Western blotting with the anti-HA antibody. * indicates a nonspecific background band.