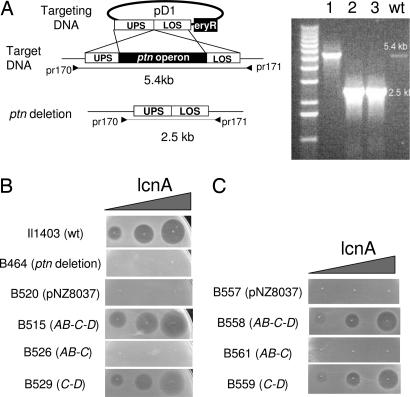
Fig. 2.
Deletion and complementation studies of the man-PTS operon. (A) Deletion of the ptnAB-C-D operon was obtained through a double cross-over event between the chromosome (target DNA) and the targeting plasmid (pD1). pD1 is composed of four modules: upper flanking sequence (UPS; 1kb), lower flanking sequence (LOS; 1.2 kb), the eryR unit for selection, and pCR-TOPO as vector. The double cross-over event was verified by PCR, using the primer pair pr170 and pr171. As shown (Right), the mutant clones (lanes 2, 3) gave rise to a 2.5-kb PCR product, whereas the WT and a revertant (lane 1) yielded the full-length (5.4 kb) product. (B) Sensitivity of the various L. lactis clones to lactococcin A: Il1403 (WT strain), B464 (ptn deletion mutant), B520 (ptn deletion mutant expressing the empty vector), B515, B526, B529, ptn deletion mutants expressing cloned ptnAB-C-D, ptnAB-C, and ptnC-D, respectively. (C) Sensitivity of L. sakei Lb790 derivatives to lactococcin A: B557 expressing the empty vector, B558, B561, and B559, expressing the lactococcal ptnAB-C-D, ptnAB-C, and ptnC-D, respectively. Nisin (5 ng/ml) was used to express cloned genes in lactococcal clones, whereas in Lactobacillus clones, where leakage in gene expression was sufficient for our purpose, nisin was omitted. In B and C, increasing amounts of lactococcin A (0.5, 5, and 50 BU) were directly spotted onto lawns of indicator cells. Growth inhibition by bacteriocin is seen as clear zones.