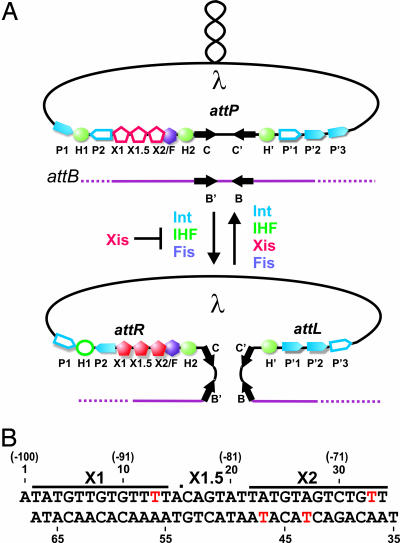
Fig. 1.
Integrative and excisive recombination of phage λ. (A) Schematic representation of the phage λ site-specific recombination reactions. The supercoiled phage genome inserts into the E. coli chromosome by recombination between the attP (phage) and attB (bacterial) sites to generate the attL and attR sites that are substrates for excisive recombination. Proteins required for integration and excision are indicated: Int, integration host factor (IHF), and factor for inversion stimulation (Fis). Excise (Xis) is required for excision and inhibits integration. Filled symbols, binding sites used; open symbols, binding sites not used during the integration or excision reactions (1). (B) Xis binding sequence used to form crystals with red nucleotides depicting 5-bromo-uracil substitutions used for phasing. The dot between nucleotides 15 and 16 represents a nick in the DNA present after annealing the three oligonucleotides. The nucleotide numbers in parentheses are relative to the center of the attR core site, and the lines represent the conventional binding sites based on in vitro footprinting data and DNA sequence relationships (40).