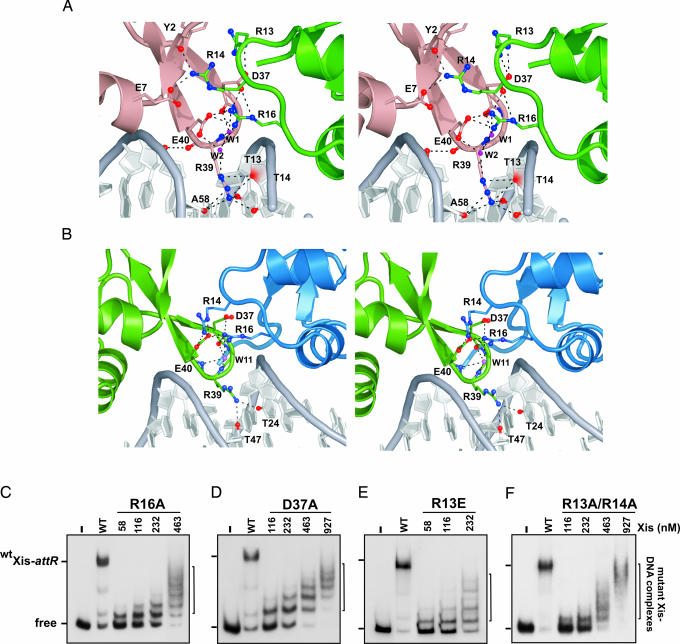
Fig. 4.
Protein–protein interactions stabilize a nucleoprotein filament. (A and B) Cross-eyed stereoviews of residues within Xis–Xis interfaces involved in hydrogen bonding or ionic interactions in the Xis cooperative complex. (A) The interface between the Xis monomers bound at X1 (dark salmon) and X1.5 (green). (B) The interface between Xis monomers bound at X1.5 (green) and X2 (blue). (C–F) The effects of mutations in the Xis protein interfaces. Each panel shows a titration of the Xis mutant on the 263 attR fragment (−220 to +43) used in Fig. 2A. The identity of the Xis mutant is indicated at the top: R16A (C), D37A (D), R13E (E), and a double R13A and R14A mutant (F). The lanes designated WT contained reactions using 116 nM WT Xis; − designates that no Xis was added. Data shown for the R16A mutant are modified from figure 5C of ref. 13.