TABLE 1.
Genotypes and genotypic values of populations and data sets
| Population and data seta | RIL genotypeb | Genotype of the population/data set | Genotypic valuec | Half of the QQ vs. qq contrast [(QQ − qq)/2]: |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIL | P + a | |||
| P − a | c0 = (2a)/2 = a | |||
| TC(B) | P + d | |||
| P − a | c1 = (a + d)/2 | |||
| TC(H) | P + a | |||
| P + d | c2 = (a − d)/2 | |||
| TC(F) | 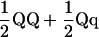 |
 |
||
 |
 |
c3 = a/2 | ||
| SUM | QQ + Qq | 2P + a + d | ||
| Qq + qq | 2P − a + d | cSUM = (2a)/2 = a | ||
| TC(B) Hmp |  |
 |
||
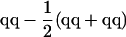 |
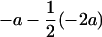 |
 |
||
| TC(H) Hmp | 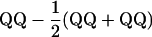 |
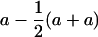 |
||
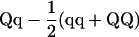 |
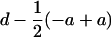 |
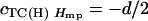 |
||
| DIFF | QQ − Qq | a − d | ||
| Qq − qq | a + d | cDIFF = (−2d)/2 = −d |
Populations are the RILs, their corresponding testcrosses to B73 parent [TC(B)], to H99 parent [TC(H)], and to the F1 hybrid [TC(F)]. Data sets were obtained by the sum TC(B) + TC(H) [SUM], the difference TC(H) − TC(B) [DIFF], the midparental heterosis (Hmp) of each TC(B) [TC(B) Hmp = TC(B) − MP, where MP = (RIL + B73)/2] and each TC(H) [TC(H) Hmp = TC(H) − MP, where MP = (RIL + H99)/2].
Q, QTL allele of H99; q, QTL allele of B73.
P, mean of the two QQ and qq homozygotes; a, additive effect; d, dominance effect. a has been defined as  (H99 − B73), and it is positive when H99 has the highest value.
(H99 − B73), and it is positive when H99 has the highest value.
