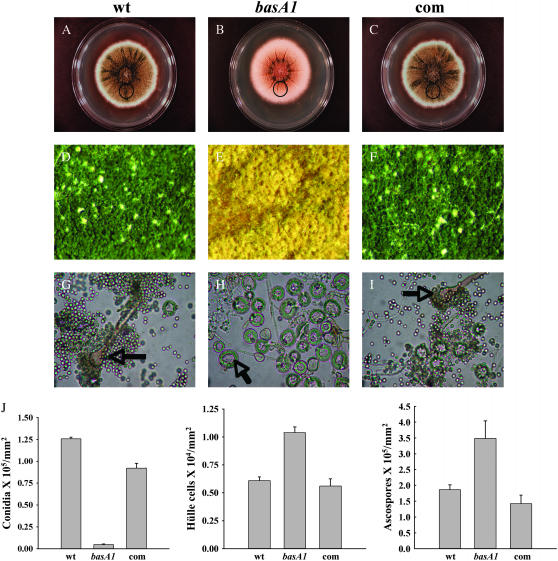
Figure 5.—
Comparison of asexual and sexual differentiation between wild type and the basA1 mutant. Conidiospores of A28 (wt), basA1 mutant, or complementation strain (com) were inoculated at the center of YGT plates and incubated at 28° in constant dark for 7 days. (A–C) Images of full colonies. (D–F) Images of growth in the area 3.5 cm away from the inoculation origin (circled area in A–C) under a dissecting microscope with a ×6 objective. Conidiophores (in G and I) and Hülle nursing cells (in H) are labeled with arrows, respectively. (G–I) Samples were collected, crushed, and fixed. Images in G–I were captured under a light microscope with a ×40 objective. (J) Quantitative comparison of conidiospore, Hülle cell, and ascospore production among wild type, basA1 mutant, and complementation strain. Quantitative comparison of ascospore production among wild-type, basA1 mutant, and complementation strain was done 10 days after inoculation. Samples were harvested from circled regions in A–C.