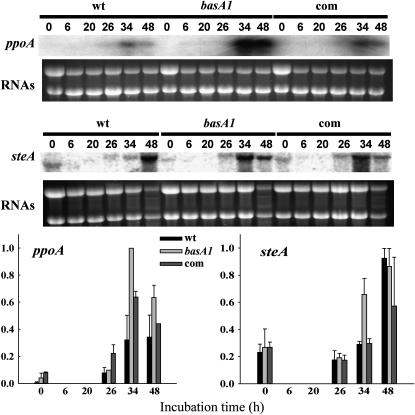
Figure 8.—
Effects of the basA mutation on the transcription of developmental genes in A. nidulans. The wild-type strain A28, the basA1 mutant 8-145, and the complementation strain were cultured in shaken conditions in YGT liquid medium for 20 hr and then shifted onto solid YGT medium. At that time, plates were sealed with parafilm and incubated at 28° in the dark to induce sexual development for 20 hr. Total RNA corresponding to wild type and basA1 strains was isolated at the time of the shift (t = 0), at 6 and 20 hr (during sexual development induction), and at 26, 34, and 48 hr after the shift (6, 14, and 28 hr after sexual development induction, respectively). Transcriptional levels of ppoA and steA were examined by Northern analysis. rRNAs stained with ethidium bromide are shown to indicate RNA loading. The experiment was repeated twice with similar results (average values are shown). Relative transcript levels were quantified by densitometry using Scion Image Beta 4.0.2.