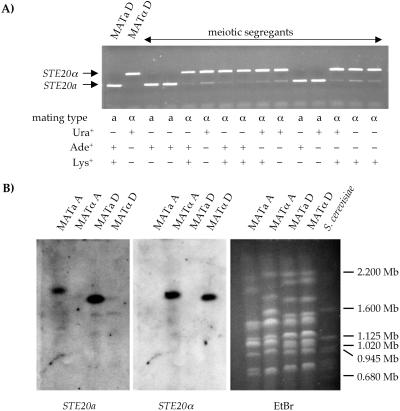
Figure 2.
The STE20a gene is MATa mating-type specific. (A) Progeny of a cross between the serotype D MATa strain MCC3 (cna1∷ADE2 ade2 ura5) and the MATα strain JEC170 (ade2 lys2) were isolated and mating type was determined by PCR analysis and genetic backcrosses. The molecular analysis of mating type was performed by PCR amplification of the MATa or MATα-specific allele of the STE20 gene. The MATa-specific PCR product was loaded on a standard agarose gel and run for ≈15 min before the MATα-specific reactions were loaded into corresponding wells. Under these conditions, some weak crossreactivity of the STE20a-specific primers was observed with DNA from MATα strains. Mating type of the meiotic segregants was determined by genetic backcrosses and is indicated below the gel. In addition, progeny were tested for recombination by scoring auxotrophic markers inherited from the parental strains. (B) Chromosomes from the serotype A strains 125.91 (MATa) and H99 (MATα), the serotype D congenic pair of strains JEC20 (MATa) and JEC21 (MATα), and S. cerevisiae (size marker) were separated by pulsed-field electrophoresis, and the gel was stained with ethidium bromide (Right). The chromosomes were then blotted onto a nylon membrane, and Southern hybridizations were performed by using probes specific to the serotype D STE20a or STE20α genes (Left and Center). Identical results were obtained by using probes derived from serotype A-specific DNA (data not shown).