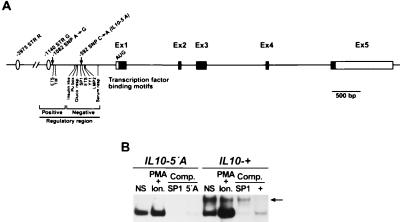
Figure 1.
Map of the human IL10 gene on chromosome 1q31-32 (38–40). Exons, AUG start, untranslated regions, and SNP and STR polymorphisms are shown along with putative transcriptional factor-binding sites identified by sequence homology (41) in relation to negative and positive regulatory elements. (B) Differential DNA-protein binding between synthesized oligonucleotide probes specific for IL10-5′A vs. IL10-+. Synthetic oligonucleotides 25 base pairs around position IL10-592 were incubated with nuclear extracts of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from random human donors and tested in an electrophoretic mobility shift assay for specific DNA-binding recognition factors (see text). Both allele nucleotides, IL10-+ and IL10-5′A, resolve the faster-migrating SP-1 complex, but only IL10-+ specifically binds the slower-migrating complex (arrow). NS, nonstimulated; Comp, cold competition with double-stranded oligonucleotides; PMA, phorbolmyristate acetate; Ion, ionomycin. Comparable results were obtained in duplicate analyses with three human donors of nuclear extracts.