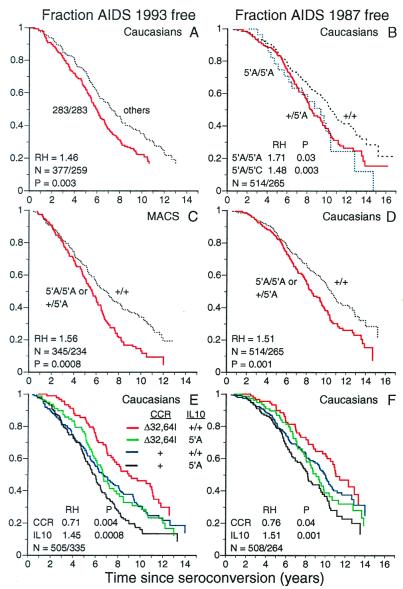
Figure 2.
Survival analysis of STR and SNP variants of IL10 in AIDS cohorts. Number of patients and number of events (n), P value (P) and RH based on the Cox proportional hazards model are given. (A) Individuals homozygous for IL10-R(−3975)−283/283 compared to those bearing any other STR allele genotypes in progression to AIDS-1993 among Caucasians. (B) Kaplan–Meier survival curves demonstrating time to AIDS-1987 were examined from combined Caucasian cohorts based on IL10-5′−592A (abbreviated IL10-5′A), genotypes: IL10-+/+; IL10-+/5′A, and IL10-5′A/5′A. (C) Dominant model IL10-+/+ vs. IL10-+/5′A plus 5′A/5′A tested in Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study cohort for time to AIDS-1993. (D) Same as C for combined Caucasian cohorts to AIDS-1987. (E and F) Kaplan–Meier survival curve demonstrating the interactive influence of dominant susceptible IL10-5′A-bearing genotypes and CCR2-64l- or CCR5-Δ32-bearing genotype dependence of time to AIDS-1993 (E) and AIDS-1987 (F) in combined Caucasian cohorts. Numbers of patients/AIDS events, P value (P) and RH based on the Cox proportional hazards model are given. Cox models are based on combined analysis that considered IL10-5′A and CCR5-Δ32/CCR2-64l effects together. RH and P values represent analyses where CCR5/2 protective genotypes are assessed in a Cox model with IL10 genotypes treated as covariables and vice versa.