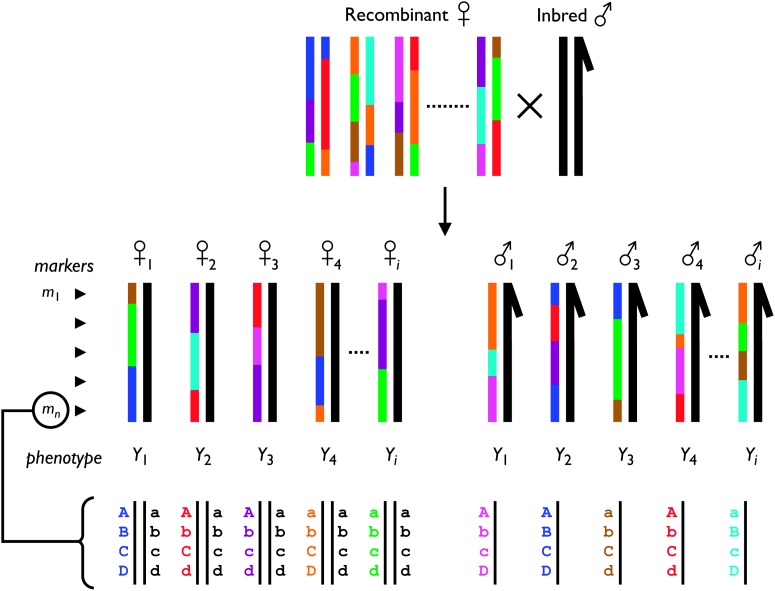
Figure 2.—
Overview of the experimental strategy. Virgin females from the synthetic D. melanogaster mapping population (colored mosaic chromosomes) are crossed to males of the isogenic strain of D. melanogaster used for genome sequencing (uniform black chromosomes). All F1 progeny from this cross are trans-heterozygotes of a maternally inherited synthetic recombinant chromosome against a paternally inherited chromosome from the isogenic strain. Male F1 are hemizygous for the recombinant X chromosome. F1 trans-heterozygotes are each phenotyped for the trait of interest and genotyped for a set of molecular markers spanning the chromosome(s). As shown, a marker represents a multilocus genotype from a set of nonrecombining SNPs (four in this example). Markers allow the eight lines founding the recombinant population to be distinguished. Only the sex chromosomes are presented in this figure—autosomes would behave similarly to female X chromosomes.