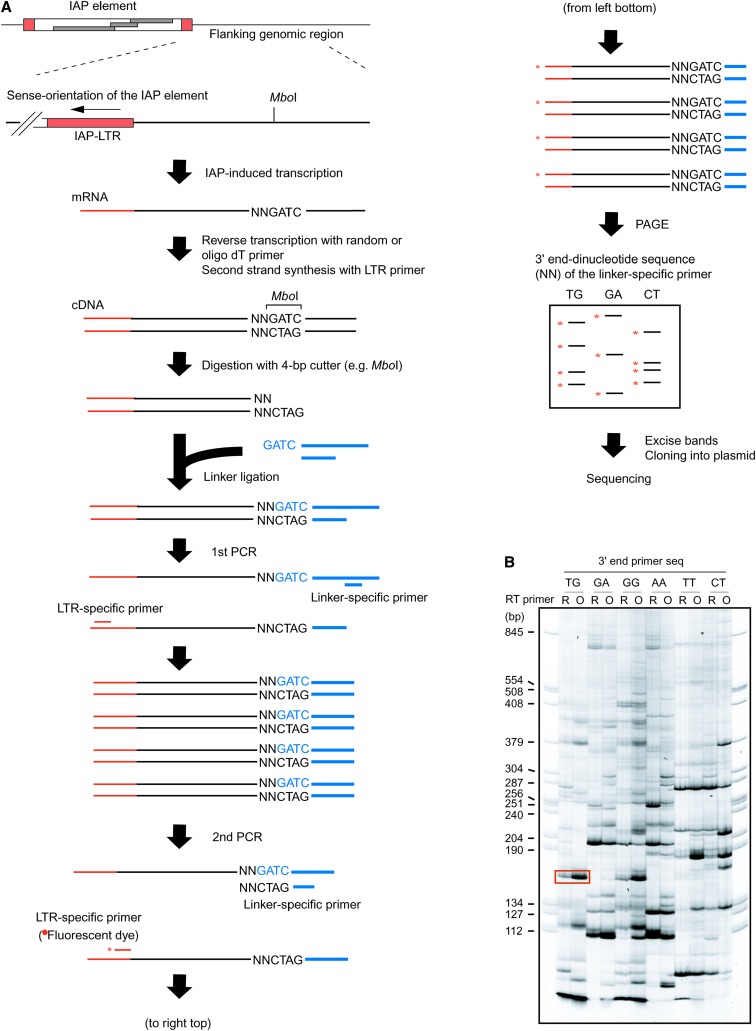
Figure 3.—
Screening for IAP-induced transcripts. (A) Procedure for the isolation of IAP-induced transcript. Total RNA from clone I-D1 expressing IAP-induced GFP transcript (Figure 2) was analyzed. As shown in B and Figure 4, detection of IAP-induced GFP transcript serves as a positive control for the experimental procedure. Following reverse transcription and second-strand synthesis, cDNA was digested with a 4-base cutter restriction enzyme (MboI is shown as an example) and ligated with a linker DNA. The cDNA was amplified by nested PCR with LTR-specific primer and linker-specific primer and separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). The linker-specific primer in the second PCR contains the restriction site sequence and selective dinucleotide (shown by “NN”) at the 3′ end. The specific dinucleotide sequence was used in each second PCR and only cDNA fragments that contain the same dinucleotide sequence next to the restriction site were amplified. As a result, only a subset of the cDNA fragment was amplified in each reaction, resulting in improvement of the resolution of PCR products in PAGE analysis. The LTR-specific second PCR primer was fluorescent labeled (asterisk) for visualization. (B) PAGE analysis of the PCR products. A representative PAGE image utilizing six different linker-specific second PCR primers is shown here and the list of linker-specific second PCR primers is presented in supplemental Table S2 at http://www.genetics.org/supplemental/. The band corresponding to the predicted size of IAP-induced GFP transcript is boxed. R, random primer; O, oligo(dT) primer.