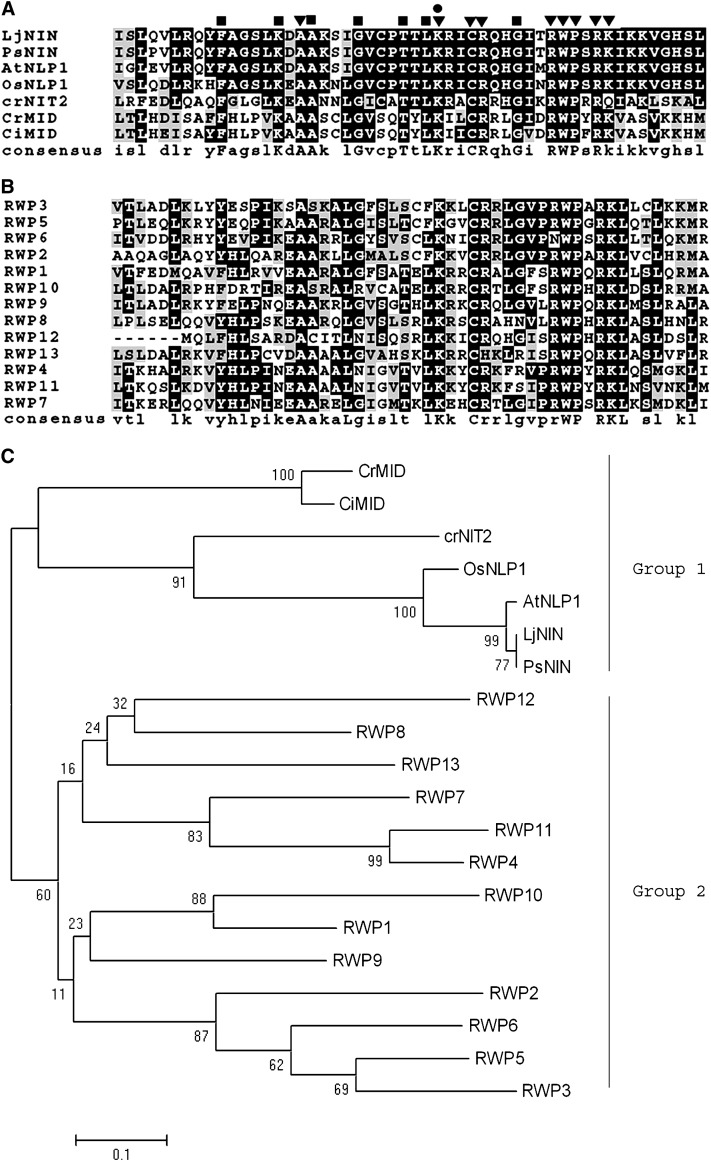
Figure 1.—
RWP-RK proteins. (A) Alignment of RWP-RK domains from C. reinhardtii Mid (CrMid, AAC49753), C. incerta Mid (CiMid, AAB60944), C. reinhardtii Nit2 (CrNit2, ABC42493), and several Nin-like plant proteins: Lj, L. japonicus (CAB61243); Ps, Pisum sativum (CAD37949); At, Arabidopsis thaliana (F84548); Os, Oryza sativa (AAM22710.1). ▾, conserved amino acids within all listed proteins (except in CrNit2, in which lysine in RWP-RK is replaced by glutamine); •, mutation of this amino acid from lysine to isoleucine in mid-1 mutant leads to pseudo-plus gametes; ▪, conserved amino acids within all proteins listed in A but not in B. (B) Alignment of Chlamydomonas RWP proteins. (C) Neighbor-joining tree showing the relationship of all listed RWP-RK proteins. Numbers at nodes represent bootstrap percentages of 1000 repeated runs. Proteins in group 1 all respond to nitrogen limitation in different organisms; the function of proteins in group 2 is currently unknown.