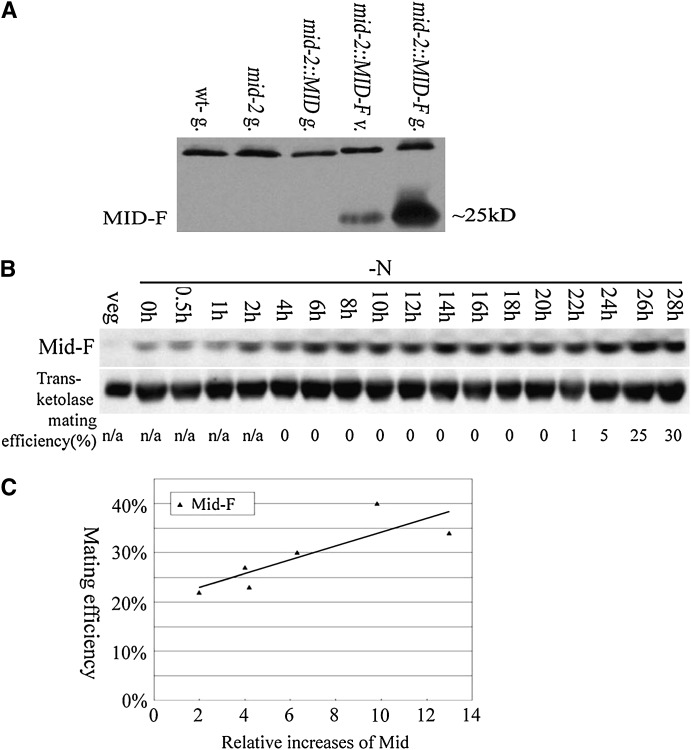
Figure 3.—
Mid protein levels related to minus mating efficiency. (A) An anti-FLAG antibody was used to detected FLAG-tagged Mid in mid-2∷MID-F cells. Gametes from wild-type minus, mid-2, and mid-2∷MID (a mid-2 transformant carrying MID without FLAG tag) were used as negative controls. The top ∼35-kDa band in all lanes was due to cross-hybridization between the anti-FLAG antibody and an unknown Chlamydomonas protein and served as a loading control. (B) mid-2∷MID-F expression in synchronous culture. The anti-FLAG antibody was used to detect Mid-FLAG; an anti-transketolase antibody was used to detect transketolase as an internal control. Mating efficiencies of cells when samples were collected were standardized using mating efficiencies of wild-type tester cells. (C) Relationship between the amount of Mid-F and the mating efficiency of mature mid-2∷MID-F cells. Six individual mid-2∷MID-F subclones were grown synchronously and the mating abilities of individual subclones were tested at 28 hr after nitrogen removal. The increases of Mid-F levels at 28 hr were obtained by quantitation of the Mid-F protein signal with the transketolase signals and standardized by the relative amount of Mid in corresponding vegetative cells. The relative increases of Mid-F were plotted against the mating efficiency of individual mid-2∷MID-F subclones.