Figure 8.
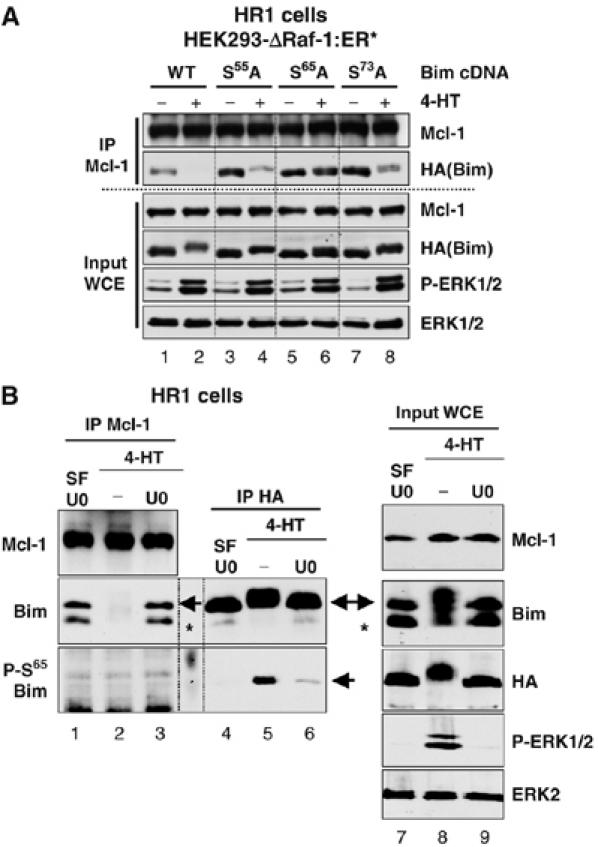
ERK1/2-dependent phosphorylation of BimEL at Ser65 is required for dissociation of BimEL from Mcl-1. (A) HR1 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding HA-BimEL (WT), or HA-BimEL with individual point mutations at Ser55Ala, Ser65Ala or Ser73Ala. After 24 h, cells were serum starved for 6 h before treating for a further 15 min with 100 nM 4-HT to activate ERK1/2. Whole-cell extracts (input WCE) were used for immunoprecipitation of Mcl-1 and samples were then immunoblotted with antibodies to Mcl-1, HA(Bim), P-ERK1/2 and ERK1/2. (B) HR1 cells were transfected with HA-BimEL. Twenty-four hours later, cells were serum starved for 1 h in the presence of 20 μM U0126 to inactivate ERK1/2. Cells were then washed thoroughly and stimulated with 100 nM 4-HT±20 μM U0126 for 1 h. Whole-cell extracts (input WCE) were used to immunoprecipitate Mcl-1 or HA-BimEL. Samples were then immunoblotted with antibodies to Mcl-1, HA(Bim), Bim, Phospho-Ser65-Bim, P-ERK1/2 and ERK1/2. The arrowheads indicate the position of the HA-BimEL, while the asterisk indicates the position of the endogenous BimEL. Note that ΔRaf-1:ER* induces phosphorylation of BimEL at Ser65, but phospho-Ser65-BimEL is not detected in Mcl-1 IPs.
