Figure 1.
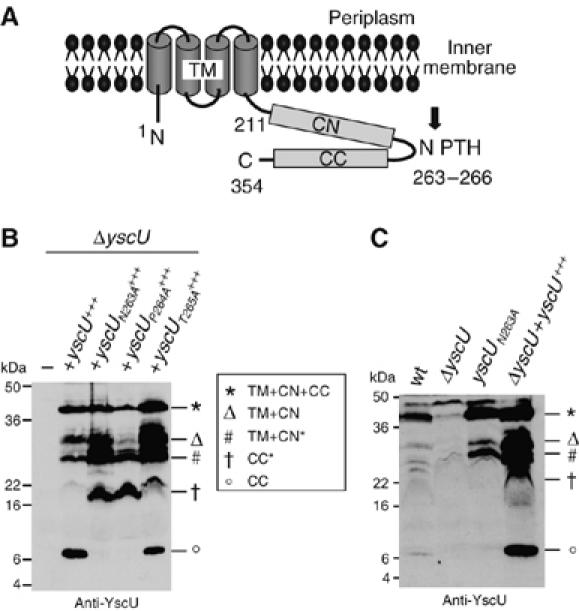
(A) Schematic representation of YscU based on studies by Allaoui et al (1994) and Lavander et al (2002). Letters indicate N-terminus (N), C-terminus (C), conserved NPTH motif (NPTH), transmembrane domain (TM, residues 1–210), N-terminal half of the cytoplasmic domain (CN, residues 211–263) and the C-terminal half of the cytoplasmic domain (CC, residues 264–354). Numbers indicate amino-acid positions in YscU from Y. enterocolitica W22703 (NCBI NC_002120). The black arrow represents the putative cleavage site at the NPTH motif. (B) Total membrane proteins of Y. enterocolitica E40 ΔyscU mutant bacteria, complemented in trans with wt or mutated alleles under the arabinose inducible pBAD promoter, were purified after 4 h of induction of the yop regulon and analyzed by immunoblot with anti-YscU antibodies. The different forms of YscU are indicated as follows: YscU (star), YscUTM+CN (triangle), YscUCC (circle), YscUTM+CN* (#) and YscUCC* (cross). The latter two result from cleavage at the alternative site. (C) Total membrane proteins of the indicated Y. enterocolitica strains. Strains and plasmids used: wt (pYV40); ΔyscU (pLY4001); yscUN263A, mutation inserted at the yscU locus (pISO4007); yscU+++ (pLY7); yscUN263A+++ (pSTW7); yscUP264A+++ (pSTW8); yscUT265A+++ (pSTW9).
