Figure 1.
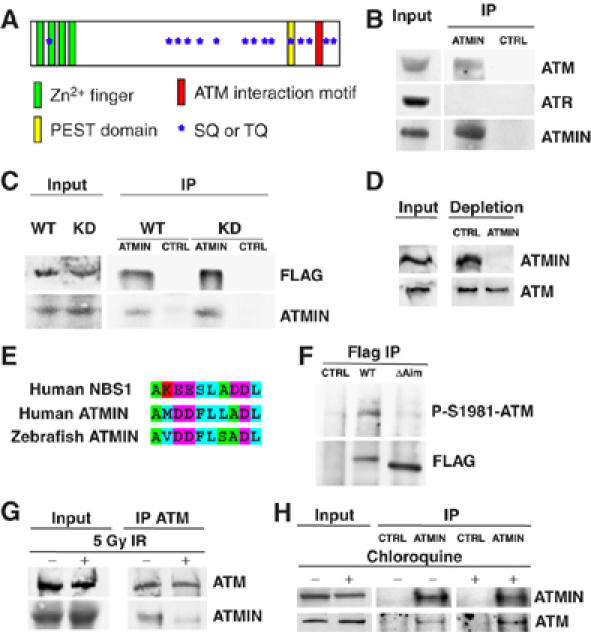
ATMIN interacts with ATM. (A) Schematic representation of the ATMIN protein. Approximate regions of ATMIN encoding Zn2+ fingers are indicated by green boxes, the PEST domain as a yellow box, the ATM interaction motif as a red box, SQ/TQ motifs as blue stars. (B) ATMIN immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed with HCT116 cell lysates followed by immunoblotting with antibodies specific for ATM, ATR and ATMIN. (C) HEK 293T cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged wild-type ATM (WT) or FLAG-tagged kinase-dead ATM (KD), ATMIN IP was performed, followed by immunoblotting with FLAG and ATMIN-specific antibodies. (D) HEK 293T cell protein extracts were depleted of ATMIN protein or control depleted, followed by immunoblotting with ATMIN- and ATM-specific antibodies. (E) Alignment of the ATM interaction motifs of human NBS1, human ATMIN and zebrafish ATMIN. Amino acids are coloured according to biochemical properties (hydrophobic, blue; acidic, purple; basic, red; polar, green). (F) FLAG IP was performed on HEK 293T cell lysates transfected with control vector, FLAG-tagged wild-type ATMIN or ATMINΔAim, followed by immunoblotting with FLAG- and P-S1981-ATM-specific antibodies. (G) HEK 293T cells were irradiated with 5 Gy or mock treated, ATM IP was performed, followed by immunoblotting with ATMIN and ATM antibodies. (H) HEK 293T cells were treated with 25 μg/ml chloroquine (4 h) or mock treated, ATMIN or control IP was performed, followed by immunoblotting with ATMIN and ATM antibodies.
