Figure 1.
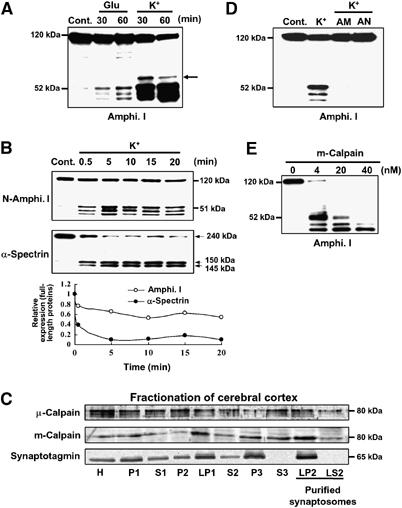
High K+ induces multiple amphiphysin I (Amphi. I) cleavages by calpain in mouse hippocampal slices. (A) Western blotting analysis of hippocampal slices stimulated with L-glutamate or high K+ and then allowed to rest for the indicated times. Probing with anti-amphiphysin I antibody recognizing the N terminus demonstrated the presence of three truncated forms of amphiphysin I. Arrow, fourth truncated form of amphiphysin I. (B) Time-dependent cleavages of amphiphysin I and α-spectrin after high K+ stimulation of hippocampal slices for the indicated times. The lowest panel shows the quantitative analysis of the expression changes of FL amphiphysin I and α-spectrin after high K+ stimulation. The expression levels of both proteins of the control (time=0 min) were set at 1. (C) Subcellular fractionation of μ- and m-calpain from cerebral cortex as shown by probing with anti-μ- and m-calpain antibodies. Anti-synaptotagmin antibodies were used to monitor synaptosomal fractions. H, total homogenate; P2, crude synaptosomal pellet; LP2, membrane fraction of purified synaptosomes; LS2, cytosol fraction of purified synaptosomes. (D) Anti-amphiphysin I immunoblotting showing that calpain inhibitors, ALLM (AM) or ALLN (AN), blocked high K+-induced amphiphysin I cleavage. (E) Anti-amphiphysin I immunoblotting showing the in vitro cleavage of recombinant amphiphysin I (0.5 μg/μl) by various concentrations of recombinant m-calpain.
