Figure 5.
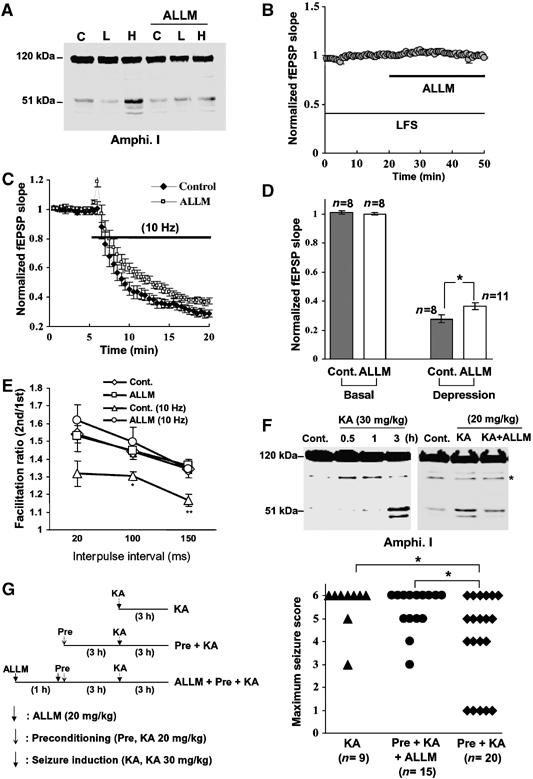
Amphiphysin I cleavage by calpain inhibits excessive synaptic transmission in hippocampal slices and in vivo. (A) Anti-amphiphysin I immunoblot showing the effects of either no electrical stimulation (C), LFS (L, 0.03 Hz) or HFS (H, 10 Hz) on calpain-dependent amphiphysin I cleavage in mouse hippocampal slices, without or with ALLM preincubation. (B) ALLM inhibition of calpain had no effect on fEPSP slope during LFS. (n=7) (C) Effect of calpain inhibition (ALLM) on fEPSP depression induced by HFS. Control, n=8; ALLM, n=11. (D) Comparison of fEPSP slopes at 15 min after LFS and HFS in the ALLM-perfused slices and controls. *P<0.05. (E) PPF in hippocampal slices following LFS is reduced following HFS, an effect that is blocked by inhibiting calpain with ALLM. ALLM had no effect on PPF following LFS. The data represent the ratios of the second EPSP slopes versus the first fEPSP slopes separated by the given intervals. As a control, hippocampal slices were incubated with DMSO instead of ALLM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with Cont. n=10–15. (F) Anti-amphiphysin I immunoblot showing the ability of KA injections to induce calpain-dependent amphiphysin I cleavage in the hippocampus of FVB/NJ mice. Preincubation with ALLM inhibited the KA-induced cleavage of amphiphysin I. *Nonspecific band. (G) Preconditioning with low-dose KA prevented KA-induced development of seizures in the FVB/NJ mice and ALLM inhibited the preconditioning effect. Left panel, schematic time schedule of the animal experiments. Right panel, the maximum seizure score in mice of each group. Seizure scores were monitored for 3 h after KA (30 mg/kg) injection as described in ‘Methods'. *P<0.05.
