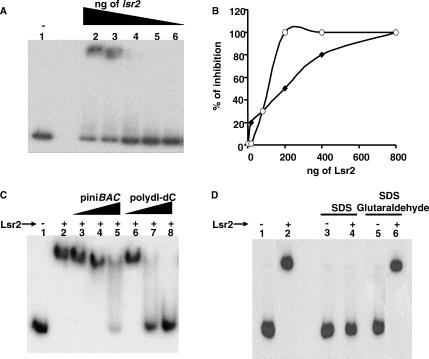
Figure 7. DNA Binding Properties of Lsr2.
(A) EMSA assay of radiolabeled PiniBAC in the presence of Lsr2. Five fmole (0.7 ng) of PiniBAC were incubated with the following amounts of Lsr2: lane 1, 0 ng; lane 2, 400 ng; lane 3, 200 ng; lane 4, 100 ng; lane 5, 50 ng; lane 6, 25 ng.
(B) Determination of the Kd of Lsr2-binding activity to PiniBAC. Five fmole (♦) and 50 fmole (○) of radiolabeled PiniBAC were incubated with the following amounts of Lsr2: 0 ng, 50 ng, 100 ng, 200 ng, 400 ng, and 800 ng; and then analyzed in EMSA assays.
(C) Competition analysis. Fifty fmole of radiolabeled PiniBAC were incubated with 200 ng of Lsr2 where indicated. Different amounts of either cold PiniBAC or poly dI-dC were then added as competitors. Lane 1, no Lsr2 (all other lanes contain Lsr2); lane 2, no competitor; lane 3, 7 ng of PiniBAC; lane 4, 37 ng of PiniBAC; lane 5, 72 ng of PiniBAC; lane 6, 7 ng of poly dI-dC; lane 7, 37 ng of poly dI-dC; lane 8, 72 ng of poly dI-dC.
(D) Specificity of DNA binding. Five fmole of radiolabeled PiniBAC were incubated with 200 ng of Lsr2 where indicated by a “+” followed by treatment with 0.5% SDS or SDS plus 0.1% glutaraldehyde where indicated. Lane 1, radiolabeled PiniBAC only; lane 2, Lsr2 added; lane 3, SDS only; lane 4, Lsr2 plus SDS; lane 5, SDS plus glutaraldehyde only; lane, 6 Lsr2 plus SDS and glutaraldehyde.