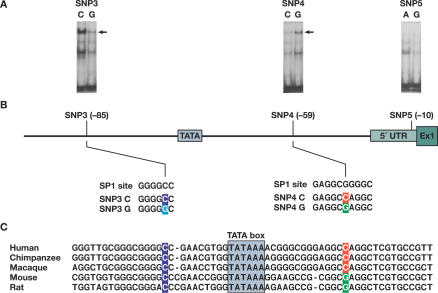
Figure 5. Binding Affinity of Nuclear Factors to the SNP-Containing Fragments in the 5′ Regulatory Regions of PPIA and the Sequence Context of the Region.
(A) Gel shift analysis of SNP3, SNP4, and SNP5 in the 5′ regulatory region of PPIA. Nuclear extracts from human T lymphocytes induced by IL4 were bound to the DNA fragment containing the C or G allele of SNP3, the C or G allele of SNP4, and the A or G allele of SNP5, respectively. The arrowhead indicates the band showing differential binding of nuclear factor(s) to the oligonucleotides. The bands below the arrow may represent nonspecific complexes and the bands at the bottom are free probes.
(B) Sequence context of SNP3 and SNP4 and comparison to the consensus-binding motifs of transcription factor SP1. SNPs 3 and 4 (located at positions 1575 and 1604 in the sequence X52851, and −85 and −59, to the ATG start codon, respectively) are in perfect LD. SNP3C>G change predicts a loss of binding to a SP1 factor, while SNP4C>G change predicts a stronger binding to a SP1 factor.
(C) The interspecies alignments of a segment of the PPIA promoter containing SNP3 and SNP4. Conserved regions are underlined and SNP sites are colored.