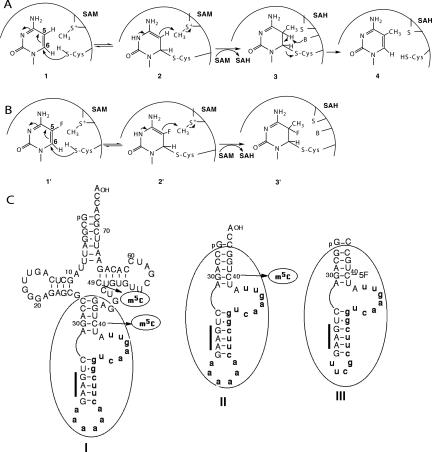
FIGURE 1.
Schemes of the mechanism for methylation of cytosine nucleosides and different substrates of Trm4p. (A) Attack by the nucleophilic thiol group of a catalytic cysteine on C6 of cytosine 1 creates a covalent intermediate 2 that serves to activate C5 as a carbanion that is stabilized by resonance. The carbanion attacks the methyl group of SAM nucleophilically, which causes the formation of a covalent methylated enzyme • nucleoside complex 3, containing 5-methyl-5,6 dihydrocytosine. Then, deprotonation of C5 leads to the m5C-containing product 4, S-adenosyl-homocysteine (SAH), and free enzyme. (B) Upon incubation with 5-fluoro-containing nucleoside 1′, the covalent intermediate 2′ is formed. Methylation of 2′ by SAM leads to trapping of the covalent 5-methyl-5-fluorohydrocytosine complex 3′ since fluorine at C5 cannot be abstracted. (C) Sequences and secondary structures of yeast tRNAPhe precursor (panel I), mini-tRNAPhe (panel II), and 36-mer FC-mini-RNA substrate analog (panel III). The intron is indicated in bold small letters and the anticodon sequence by a thick bar.