Figure 4.
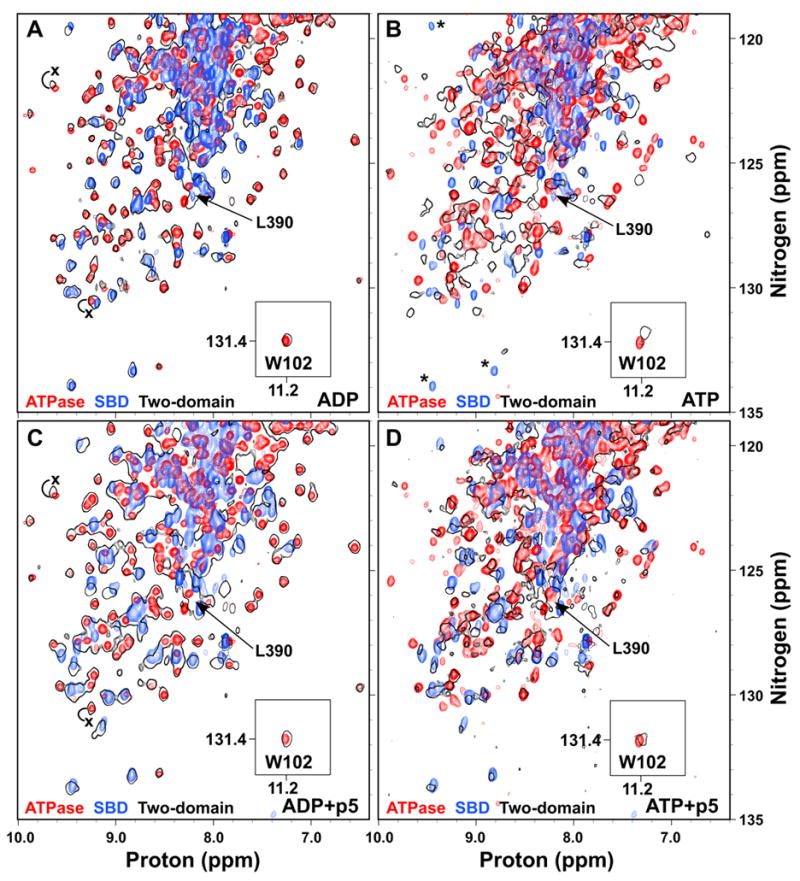
ATP binding to the two-domain DnaK protein induces domain docking that is largely reversed by substrate binding. Overlay of TROSY NMR spectra of the 15N-labeled ATPase domain (DnaK(1-388); red), SBD (H6DnaK(387-552)ye; blue) and two-domain protein (DnaK(1-552)ye; black outlines) bound to ADP (A), ATP (B), ADP and p5 peptide (C), or ATP and p5 peptide (D). The T199A mutant was used for observation of ATP states. The W102 side chain amide is shown in an inset. The ADP-bound position of L390 in the two-domain protein is indicated in all panels by an arrow. In (B), SBD residues that apparently disappear upon ATP binding to the two domain protein are indicated by asterisks. In (A) and (C), the positions of selected ATPase domain resonances that shift upon linker binding are labeled with an x at their position in DnaK(1-392).
