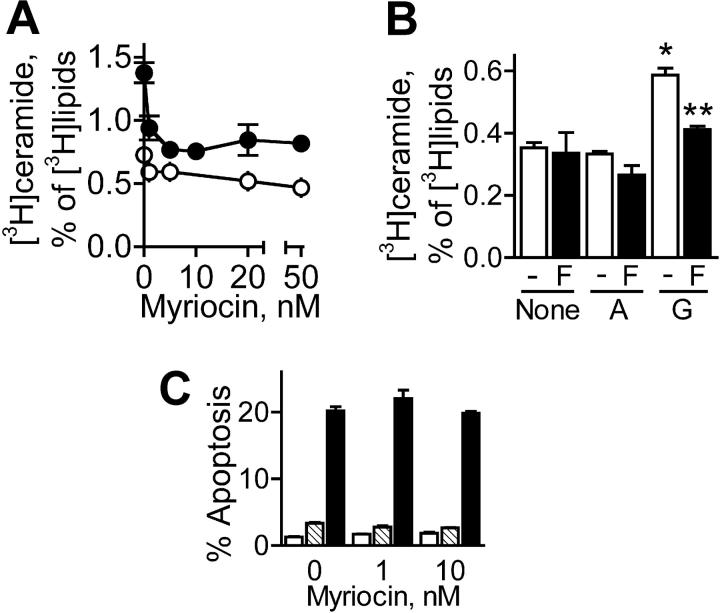
Figure 3.
Inhibitors of de novo ceramide synthesis suppress RGDfV-induced ceramide increase, but do not prevent RGDfV-induced endothelial apoptosis. (A) HBMECs (106 cells/10-cm plate) were allowed to spread on plates coated with vitronectin and blocked with 1% BSA. Cells were labeled with [3H]palmitic acid and preincubated (2 hours) with 0 to 50 nM myriocin prior to overnight incubation with RGDfV (•; 25 μg/mL) or control peptide, RADfV (○; 25 μg/mL). Ceramide was determined by TLC, as described in “Materials and methods.” P < .001 by 2-way ANOVA; n = 3. (B) HBMECs plated and labeled as in panel A were preincubated with fumonisin B1 (F; ▪; 25 μM) or vehicle control (-; DMSO; □). Then, 2 hours later RGDfV (G; 25 μg/mL), RADfV (A; 25 μg/mL), or vehicle control was added for overnight incubation. Ceramide was determined by TLC, as described in “Materials and methods.” *P = .001 compared with RADfV; **P = .001 compared with RGDfV with vehicle control; and P = .001 compared with RADfV with vehicle control, by unpaired t test; n = 3. (C) HBMECs were seeded on vitronectin-coated plates blocked with BSA. Cells were preincubated (2 hours) with myriocin prior to addition of RGDfV (▪), RADfV ( ; 25 μg/mL), or vehicle control (□). Cells were collected 24 hours later and apoptosis was assessed by PI staining. n = 3.
; 25 μg/mL), or vehicle control (□). Cells were collected 24 hours later and apoptosis was assessed by PI staining. n = 3.