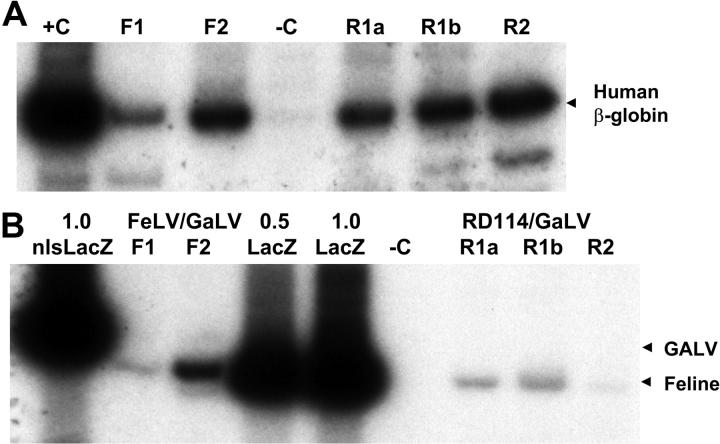
Figure 5.
Cotransduction of human S-RCs with FeLV-C and GALV or RD114 and GALV-pseudotyped retrovirus particles. Human CD34+ peripheral blood CD34+ cells were cotransduced with FeLV-C and GALV or RD114 and GALV-pseudotyped virus preparations over a 4-day period and transplanted into fetal sheep. DNA was extracted from sheep peripheral blood cells 6 months after transplantation and analyzed for the presence of human cells and the integration of the FeLV-C or RD114 and GALV-pseudotyped viruses by PCR analysis of 0.4 μg DNA. (A) Sequences from the human β-globin gene were amplified to detect the presence of human cells. F1 and F2 indicate analysis of DNA from 2 lambs infused with human CD34+ cells exposed to FeLV-C (LacZ) and GaLV (nls-LacZ) pseudotyped particles; R1a, R1b, and R2, analysis of DNA from 3 lambs infused with human CD34+ cells exposed to RD114 and GALV-pseudotyped particles; R1a and R1b, DNA from twin lambs infused with the same population of cells; –C, DNA extracted from control sheep; and +C, DNA extracted from K562 cells. (B) The relative amounts of integrated FeLV-C, RD114, and GALV-pseudotyped vectors were measured using primers that span the nls in the MFGs-nlsLacZ vector. 1.0 nls-LacZ indicates 3T3-cell DNA containing a single copy of the MFGs-nlsLacZ vector; 1.0 LacZ, 3T3-cell DNA containing a single copy of the MFGs-LacZ vector; 0.5 LacZ, 3T3-cell DNA containing a 1:1 dilution of this 1.0 LacZ DNA with untransduced 3T3-cell DNA; and –C, DNA extracted from control sheep. For quantitation, only the β-globin band and the 289-bp MFGs-LacZ and 310-bp MFGs-nlsLacZ bands were analyzed.