Figure 1.
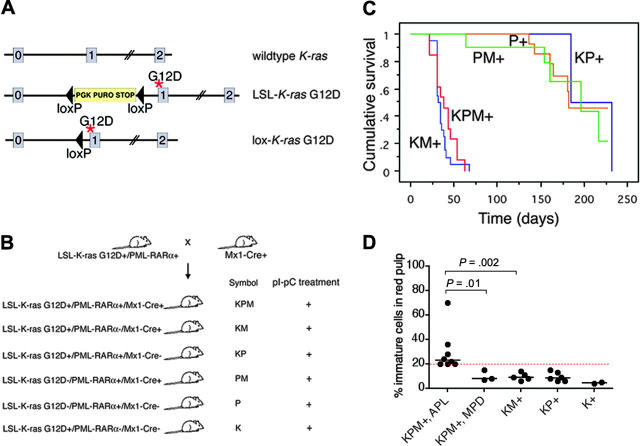
Generation of mice coexpressing oncogenic K-ras and a cathepsin G-PML-RARα transgene, survival analysis, and spleen WBC differentials. (A) Schematic of wild-type, LSL-K-ras G12D, and lox-K-ras G12D alleles, depicting K-ras exons 0, 1, and 2. Gene targeting to the endogenous K-ras locus generated the LSL-K-ras G12D allele, containing a floxed transcriptional termination codon upstream of an oncogenic mutation in codon 12 (glycine-to-aspartic acid) in exon 1. Cre recombinase-mediated excision of the stop cassette expresses the oncogenic lox-K-ras G12D allele. *G12D mutation. (B) Generation of LSL-K-ras G12D+/PML-RARα+/Mx1-Cre+ mice and controls. Progeny of crosses between LSL-K-ras G12D+/PML-RARα+ and Mx1-Cre+ mice were treated with pI-pC to generate KPM+, KM+, KP+, PM+, P+, and K+ mice. K indicates LSL-K-ras G12D; P, cathepsin G-PML-RARα; M, Mx1-Cre. + indicates pI-pC treatment. (C) Kaplan-Meier comparative survival analysis of littermate KPM+, KM+, and control KP+, PM+, and P+ mice. Analysis was performed using large numbers of mice and littermate controls to minimize strain effects. Cumulative survival is plotted against days after treatment with pI-pC for KPM+ (n = 13), KM+ (n = 20), KP+ (n = 11), PM+ (n = 12), and P+ (n = 20) mice over an observation period of more than 200 days. (D) Manual differential counts performed on 200 nucleated cells in myeloid rich sections of splenic red pulp demonstrate an increased percentage of morphologically immature myeloid cells (blasts + promyelocytes) in the spleens of KPM+ mice with APL, compared to KPM+ mice with myeloproliferative disease, KM+, nondiseased KP+, or K+ mice. Median values are represented by horizontal bars. Indicated P values are determined by Mann-Whitney test.