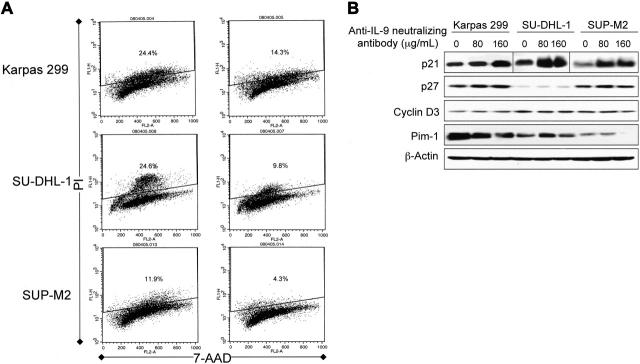
Figure 7.
Specific blockade of IL-9 induces G1 cell-cycle arrest associated with increased p21 and decreased Pim-1 kinase levels in ALK+ ALCL cells. (A) Analysis of the cell cycle using flow cytometry and PI/7-ADD staining. The right panel shows histograms of the ALK+ ALCL cells treated with 80 μg/mL anti–IL-9–neutralizing antibody compared with control cells treated with equivalent concentrations of IgG and shown in the left panel. The anti–IL-9–neutralizing antibody induces G1 cell-cycle arrest as demonstrated by the marked decrease of cells in the S phase. The number of the cells in the S phase decreased to 59%, 40%, and 36% of their corresponding baseline levels in Karpas 299, SU-DHL-1, and SUP-M2 cells, respectively. The experiment was repeated twice with consistent findings. (B) Western blot studies showing concentration-dependent increase in p21 levels after treating the ALK+ ALCL cells with 80 and 160 μg/mL anti–IL-9–neutralizing antibody. There was a simultaneous concentration-dependent decrease in Pim-1 levels in Karpas 299 and SUP-M2 cells. Whereas Pim-1 level in SU-DHL-1 cells slightly increased at a concentration of 80 μg/mL anti–IL-9–neutralizing antibody, it decreased to the baseline level at a concentration of 160 μg/mL. Significant changes were not detected in p27 and cyclin D3. β-Actin confirmed equal loading of the proteins. The results represent 1 of 2 consistent experiments.