Figure 4.
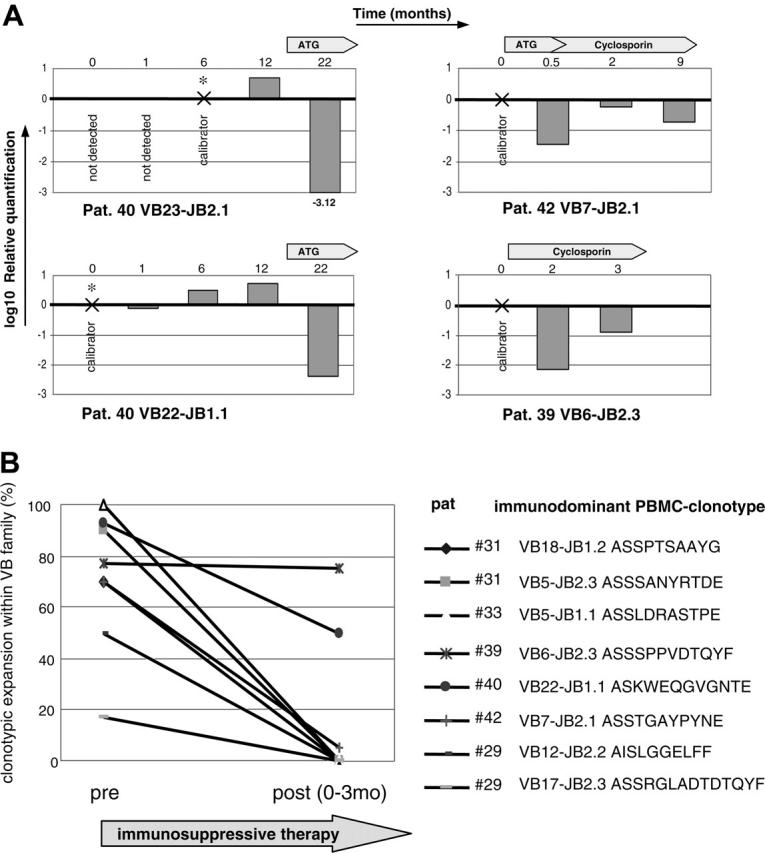
Effect of immunosuppressive therapy on TCR repertoire in AA patient. (A) For the tracking of potentially pathogenic clones, a clonotypic Taqman PCR was performed using patient CDR3-specific forward primers, CDR3-specific JB probe, and CB reverse primer. Four immunodominant clones were tracked during the course of disease in 3 AA patients. RNA was extracted from sorted CD8+ cells. For the calculation of clonotypic expression, samples in which the original immunodominant clonotype was identified were used as calibrators for subsequent or retrospective measurements. GAPDH levels were used for the normalization of RNA amounts. (B) TCR repertoire analysis was performed on 7 patients before and after application of immunosuppressive therapy that is shown in Table 3. AA patient no. 31 was analyzed before and after therapy, and 2 dominant clonotypes were found for VB5 and VB18 with the frequencies of 90% and 70%, respectively. One and 3 months after ATG therapy, normal lymphocyte count was restored and the diversity of obtained CDR3 sequences increased; furthermore, the immunodominant clonotype was not detectable by sequencing. Similar trend was seen in other patients. Patient no. 46 did not harbor any immunodominant expansions and is not shown in the figure.
