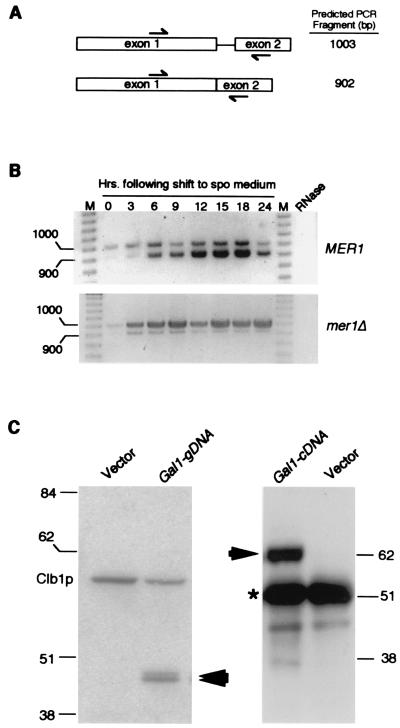
Figure 1.
AMA1 exhibits meiosis-specific transcription and splicing. (A) The AMA1 genomic locus. The arrows indicate the primer locations and predicted sizes of RT-PCR reactions with spliced and unspliced transcripts. Exon 1 contains the ORF described for SPO70 (29). (B) AMA1 is transcribed and spliced during meiosis. The RT-PCR products generated from total RNA samples taken from the wild-type and (MER1) and mutant (mer1Δ) culture during vegetative growth (0 h) and at the times indicated after transfer to sporulation medium. The molecular weight standards (M) in base pairs are indicated. The signals observed are specific for AMA1 mRNA as they are absent when the template RNA is treated with RNase A. (C) Ama1p is not synthesized in vegetative cells. Western blot analysis of soluble extracts (25 μg) or immunoprecipitates (250 μg) prepared from a wild-type strain harboring either the pGAL1-AMA1g (genomic DNA) or pGAL-AMA1c (cDNA), respectively. Ama1p-specific bands are indicated by the arrows. A 6HIS/T7 epitope-tagged Clb1p derivative served as an internal size standard and loading control. The vector lanes control for nonspecific cross hybridization of the antibody. Molecular weight standards (kDa) are given on the sides of the gels. The asterisk denotes the heavy chain present in the immunoprecipitates required for visualizing full-length Ama1p.