Figure 2.
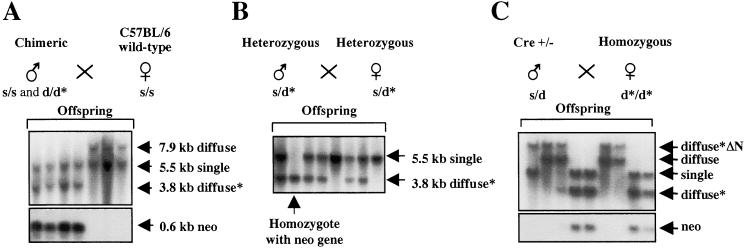
Generation and screening of mice for the mutation. (A) Chimeric males, which were derived from C57BL/6 blastocysts and targeted ES cells (diffuse haplotype), were mated with wt C57BL/6 females (single haplotype indicated by s). The wt diffuse allele is indicated by d and the mutant allele by d*. Southern blotting of the resulting offspring is shown by using the same screening strategy as in Fig. 1B, and the fragment sizes of the different alleles are indicated. The wt single allele has a different fragment size from the wt diffuse allele because of a restriction site polymorphism. Heterozygous mice (s/d* genotype) also contain a 0.6-kb neomycin PstI fragment (lower blot). (B) Mating and screening of heterozygous mice. A mouse that is homozygous for the mutation (d*/d* genotype) is indicated. All offspring with the d* allele contain the neomycin marker gene. (C) Removal of the neomycin marker gene. Homozygous mice were bred with a mouse carrying a Cre recombinase transgene (28). Mice without the marker gene contain a 12-kb PstI fragment, indicated by diffuse*ΔN. These mice are negative for the neomycin fragment (lower blot).