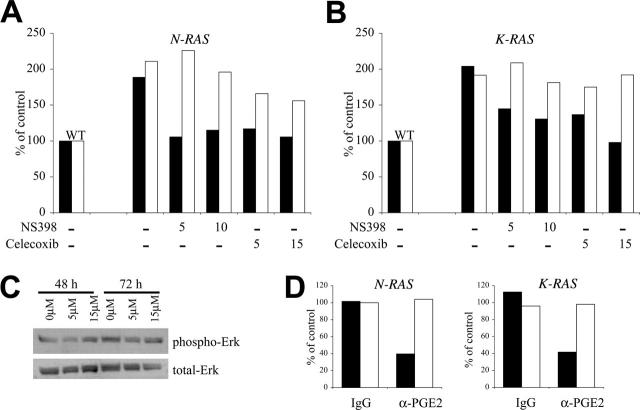
Figure 5.
Cox-2 regulates adhesion of mutant RAS MM cells to fibronectin. (A) N-RAS–containing and (B) K-RAS–containing ANBL-6 cells were treated with cox-2–specific inhibitors, NS398 or celecoxib, at the concentration shown below the bars (in μM) or DMSO control vehicle for 72 hours and then assayed for adhesion to FN (▪) or BMSCs (□). Adhesion is expressed as binding relative to WT cells where wild-type cells were arbitrarily determined to be 100%. Results reflect average binding ODs of quadruplicate samples. The experiment was repeated once with identical results. (C) Mutant K-RAS cells were cultured with celecoxib for 48 or 72 hours and protein lysates were collected. Western analysis on the lysates was performed using phospho-specific Erk (Thr202/Tyr204) antibody and total Erk antibody. No effect of celecoxib on Erk phosphorylation was observed. (D) Both N-RAS– and K-RAS–containing ANBL-6 cells were cultured in the presence of 5 μg/mL α-PGE2 neutralizing antibodies or mouse IgG isotype control for 72 hours and then assayed for adhesion to FN (▪) or BMSCs (□). The results are reported in percentage as relative adhesion of untreated N-RAS or K-RAS ANBL-6 cells cultured in parallel.